- Blog Categories
- Project Management
- Agile Management
- IT Service Management
- Cloud Computing
- Business Management
- Business Intelligence
- Quality Engineer
- Cyber Security
- Career
- Big Data
- Programming
- Most Popular Blogs
- PMP Exam Schedule for 2024: Check PMP Exam Date
- Top 60+ PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2024
- PMP Cheat Sheet and PMP Formulas To Use in 2024
- What is PMP Process? A Complete List of 49 Processes of PMP
- Top 15+ Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 170 Project Management Research Topics
- What is Effective Communication: Definition
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel in 2024?
- PMP Certification Exam Eligibility in 2024 [A Complete Checklist]
- PMP Certification Fees - All Aspects of PMP Certification Fee
- Most Popular Blogs
- CSM vs PSM: Which Certification to Choose in 2024?
- How Much Does Scrum Master Certification Cost in 2024?
- CSPO vs PSPO Certification: What to Choose in 2024?
- 8 Best Scrum Master Certifications to Pursue in 2024
- Safe Agilist Exam: A Complete Study Guide 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- SAFe vs Agile: Difference Between Scaled Agile and Agile
- Top 21 Scrum Best Practices for Efficient Agile Workflow
- 30 User Story Examples and Templates to Use in 2024
- State of Agile: Things You Need to Know
- Top 24 Career Benefits of a Certifed Scrum Master
- Most Popular Blogs
- ITIL Certification Cost in 2024 [Exam Fee & Other Expenses]
- Top 17 Required Skills for System Administrator in 2024
- How Effective Is Itil Certification for a Job Switch?
- IT Service Management (ITSM) Role and Responsibilities
- Top 25 Service Based Companies in India in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- What is Escalation Matrix & How Does It Work? [Types, Process]
- ITIL Service Operation: Phases, Functions, Best Practices
- 10 Best Facility Management Software in 2024
- What is Service Request Management in ITIL? Example, Steps, Tips
- An Introduction To ITIL® Exam
- Most Popular Blogs
- A Complete AWS Cheat Sheet: Important Topics Covered
- Top AWS Solution Architect Projects in 2024
- 15 Best Azure Certifications 2024: Which one to Choose?
- Top 22 Cloud Computing Project Ideas in 2024 [Source Code]
- How to Become an Azure Data Engineer? 2024 Roadmap
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 40 IoT Project Ideas and Topics in 2024 [Source Code]
- The Future of AWS: Top Trends & Predictions in 2024
- AWS Solutions Architect vs AWS Developer [Key Differences]
- Top 20 Azure Data Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- 25 Best Cloud Computing Tools in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Company Analysis Report: Examples, Templates, Components
- 400 Trending Business Management Research Topics
- Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK): Guide
- ECBA Certification: Is it Worth it?
- How to Become Business Analyst in 2024? Step-by-Step
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 20 Business Analytics Project in 2024 [With Source Code]
- ECBA Certification Cost Across Countries
- Top 9 Free Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates
- Business Analyst Job Description in 2024 [Key Responsibility]
- Business Analysis Framework: Elements, Process, Techniques
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Career Options after BCom to Know in 2024
- Top 10 Power Bi Books of 2024 [Beginners to Experienced]
- Power BI Skills in Demand: How to Stand Out in the Job Market
- Top 15 Power BI Project Ideas
- Top Picks by Authors
- 10 Limitations of Power BI: You Must Know in 2024
- Top 45 Career Options After BBA in 2024 [With Salary]
- Top Power BI Dashboard Templates of 2024
- What is Power BI Used For - Practical Applications Of Power BI
- SSRS Vs Power BI - What are the Key Differences?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Data Collection Plan For Six Sigma: How to Create One?
- Quality Engineer Resume for 2024 [Examples + Tips]
- 20 Best Quality Management Certifications That Pay Well in 2024
- Six Sigma in Operations Management [A Brief Introduction]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Six Sigma Green Belt vs PMP: What's the Difference
- Quality Management: Definition, Importance, Components
- Adding Green Belt Certifications to Your Resume
- Six Sigma Green Belt in Healthcare: Concepts, Benefits and Examples
- Most Popular Blogs
- Latest CISSP Exam Dumps of 2024 [Free CISSP Dumps]
- CISSP vs Security+ Certifications: Which is Best in 2024?
- Best CISSP Study Guides for 2024 + CISSP Study Plan
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker in 2024?
- Top Picks by Authors
- CISSP vs Master's Degree: Which One to Choose in 2024?
- CISSP Endorsement Process: Requirements & Example
- OSCP vs CISSP | Top Cybersecurity Certifications
- How to Pass the CISSP Exam on Your 1st Attempt in 2024?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Career Options & Courses After 12th Commerce in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- 30 Best Answers for Your 'Reason for Job Change' in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- Time Management Skills: How it Affects your Career
- Most Popular Blogs
- Top 28 Big Data Companies to Know in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Big Data Tools You Need to Know in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Web Development Using PHP And MySQL
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 30 Software Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- More
- Tutorials
- Practise Tests
- Interview Questions
- Free Courses
- Agile & PMP Practice Tests
- Agile Testing
- Agile Scrum Practice Exam
- CAPM Practice Test
- PRINCE2 Foundation Exam
- PMP Practice Exam
- Cloud Related Practice Test
- Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- AWS Solutions Architect
- AWS Developer Associate
- IT Related Pratice Test
- ITIL Practice Test
- Devops Practice Test
- TOGAF® Practice Test
- Other Practice Test
- Oracle Primavera P6 V8
- MS Project Practice Test
- Project Management & Agile
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Release Train Engineer Interview Questions
- Agile Coach Interview Questions
- Scrum Interview Questions
- IT Project Manager Interview Questions
- Cloud & Data
- Azure Databricks Interview Questions
- AWS architect Interview Questions
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Kubernetes Interview Questions
- Web Development
- CSS3 Free Course with Certificates
- Basics of Spring Core and MVC
- Javascript Free Course with Certificate
- React Free Course with Certificate
- Node JS Free Certification Course
- Data Science
- Python Machine Learning Course
- Python for Data Science Free Course
- NLP Free Course with Certificate
- Data Analysis Using SQL
- Home
- Blog
- It Service Management
- ITIL Processes and Practices in ITIL V4
ITIL Processes and Practices in ITIL V4
Updated on Apr 12, 2022 | 10 min read | 17.9k views
Share:
ITIL®, or Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is an IT service management (ITSM) framework that aligns IT services with business needs. It helps companies lower IT operating costs and raise service levels, aiming to improve business efficiency while providing high-quality service. Developed by AXELOS and released in 2019, ITIL 4 provides best practices and techniques for selecting, planning, delivering, and maintaining IT services. Professionals aiming for the ITIL 4 Foundation Certification must thoroughly understand the ITIL processes list and framework. ITIL's five revised books cover these processes and stages comprehensively.
ITIL Processes and Stages
ITIL is an ITSM framework is used by many renowned big corporates. This IT Governance Framework is made up of a variety of processes, all of which are adaptable, scalable, and customizable. These processes have a series of activities that have specific inputs, triggers, and outputs. Various ITIL® processes and the concepts that underpin them are explained in this article. The ITIL processes framework is composed of 34 processes organized into three management phases. Let’s study each stage of the ITIL processes v4 framework in greater detail to see how ITIL processes list mapped to these stages.
General Management Practices

Master Right Skills & Boost Your Career
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session

There are a total of 14 domains under this stage of ITIL V4 that have been preferred to use for service management of general management businesses. Many organizations opt for service strategy in order to figure out apt offer for the estimated target. Here, we have enlisted a brief explanation of all the domains under general management practices.
- Strategy Management: During this practice, the IT services are analyzed to determine their market position. In this process, a strategic assessment, strategy generation, strategy implementation, and measurement and evaluation are all performed sequentially.
- Service Portfolio Management: This practice is primarily concerned with the management of the available IT service portfolios. It ensures that the delivered services are in line with the objectives of the ITIL service strategy and the company’s objectives. Four sequential activities are involved in this process, which are:
- Service definition
- Service analysis
- Service approval, and
- Service charter.
- Architecture Management: It is very important to have an understanding of the different elements that are required to make an organization and this practice helps in doing so. Architecture Management assists in attaining current and future objectives efficiently by providing tools and techniques to manage major changes in a structured way.
- Service Financial Management: This practice majorly focuses on financial spending and service valuation on various services in a business including budgeting, accounting, charging activities, and many more. Accounting, budgeting, and charging for services are all part of this process, which helps the organization cover its expenses while also making a profit.
- Workforce and Talent Management: Appointing the right people with the required ITIL skills and knowledge is a must for every organization to achieve company objectives. This practice helps businesses to recruit trained professionals for the correct roles as per their qualifications, experience, and expertise with thorough planning and onboarding process.
- Continual Improvement: Business needs are dynamic, and it is significant for organizations to align their practices in accordance with service improvement, continual identification, and other related elements. Via this practice, companies can match up with the changing demand for products and services efficiently and effectively.
- Measurement and Reporting: Owing to this practice, organizations can focus on continual improvement by reducing the possibilities of uncertain situations and good decision-making at the same time. However, it depends on the relevant data collection and appropriate assessment of the same in an adequate milieu.
- Risk Management: This practice helps organizations to understand and handle risks timely without leaving any chances of facing losses in the aftermath. In order to ensure continual sustainability, it is very important to manage risks efficiently which will also create customer value.
- Information Security Management: The goal of this process is to keep the system and its data, as well as the people who have access to them, safe. In this, activities like the detection and prevention of intrusions are also included. Security requirements, assessment and implementation of information assets, policy creation, and risks are all part of this process.
- Knowledge Management: This process involves gathering and assembling useful knowledge that is further used in resolving the issues by technicians and customers. This process is made up of activities like defining knowledge management strategy, drafting knowledge, identifying and gathering data sources, editorial reviews, technical reviews, and lastly publishing.
- Organizational Change Management: Time-to-time changes in any organization are necessary to maintain constant growth and stability in general. This practice ensures the smooth and successful application of required changes and achieving contemplated benefits out of the same.
- Project Management: This practice assists organizations in the successful delivery of ongoing projects efficiently and effectively. Moreover, this can be achieved by proper planning, delegating apt resources, monitoring the process of projects' completion, and motivating the workforce throughout the stages.
- Relationship Management: Management of customer relationships, understanding customer needs, and providing services to meet those needs are all part of this process. Request and complaint handling, managing business relationships, acquiring new customers, soliciting customer feedback, and identifying opportunities are the three important activities in this process.
- Supplier Management: All supplier relationships are monitored by this process, which includes keeping track of whether or not the parties involved are adhering to their contracts and agreements. Supplier selection, evaluation, management of performance, and contract renewal/termination are the activities under this process.
Service Transition
A stage of the ITIL framework aims to bridge the gap between service design and business operations. It is characterized by thorough verification and validations, imparting training, and sharing knowledge/documentation to enable smooth operations and business continuity. The key processes include:
- Service Asset and Configuration management
- Release and Deployment Management
- Knowledge and Change Management
Service operation
The stage of the ITIL framework by which value is ultimately delivered to the customer; is characterized by process definitions, creation of standard operating procedures (SOPs), user experience, and ensuring availability, performance, and security of services. Key processes included are:
- Incident, Event, and Problem Management
- Request Management
Top Cities where KnowledgeHut Conduct ITIL Certification Training Course Online
Service Management Practices

A total of 17 domains have been added to manage under the Service Management Practices for ITSM industries in order to ensure the smooth flow of services for users and stakeholders. There are numerous services that must be monitored diligently within the organizations. Domains managed by this practice are enlisted below.
- Business Analysis: This process helps in analysing any type of business by evaluating its needs, requirements, and proposed solutions in case of uncertainties. It is important to confront the needs and business problems and solve them efficiently to create value for stakeholders and investing partners.
- Service Catalogue Management: This process primarily ensures that a current service catalogue is available with easy access to the services that customers require to remain productive. The important activities of this process are documenting service definition and description, producing and maintaining the service catalogue, and agreeing on service catalogue content.
- Service Design: This phase helps companies in determining their corporate mission and vision. This is a market-driven phase. Organizations use service strategy to figure out what services they should offer and who they should target. To achieve long-term growth and success, strategic decisions must be made when planning and delivering targeted services.
- Service Level Management: This stage entails planning for defining the overall organizational service delivery targets and then measuring their performance. Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are used to help determine service level goals and allow for easier measurement and comparison of services against actual performance. This process is made up of four sequential activities, which are understanding requirements and drafting SLAs, negotiating the SLAs, defining and standardizing the SLAs, and monitoring and reporting service performance.
- Availability Management: This procedure ensures that the customer has access to the services they always need. The sequential activities of this process are: monitoring availability, analysing availability data, investigating service unavailability, availability planning, and testing availability.
- Capacity and Performance Management: This stage ensures to keep track of services that have been delivered successfully and expected performances required from allocated resources. Along with that, satisfying the current and future demands while saving costs at the same time.
- Service Continuity Management: It is important for businesses to ensure that the services they are offering are available at the time of need and expected performance during uncertainties. This practice helps in building a framework for an organization's stability in order to keep the interest of key stakeholders on point while maintaining its reputation and brand value.
- Monitoring and Event Management: Via this stage, organizations can observe the services that have been offered and prepare a report on the current identified state as an event. The report is made by recognizing business processes, services, infrastructure, and information security events, and giving proper responses to the same including potential faults.
- Service Desk: It acts as a gateway for recording incidents or service requests and connects to the apt service provider in order to resolve the issues on time. There should not be any other point of contact except the 'Service Desk' for a smooth process.
- Incident Management: In the event of a malfunctioning printer, a lost or forgotten password, or some other type of error message, this procedure immediately restores service. Identifying and classifying the incident, prioritizing, investigating and diagnosing, resolving, and concluding the investigation are all steps in this process.
- Service Request Management: This practice helps to support the communicated service quality by monitoring service requests that have been generated by the users on time and ensuring no such situation will be repeated in the future.
- Problem Management: A primary goal of this process is to identify and prevent future incidents and problems. Detection and logging of problems, categorization, investigation and diagnosis, and problem resolution and closure are the first four steps in this process.
- Release Management: Every organization comes up with changes in services or issues a new set of services from time to time. Through this practice, businesses can create a smooth flow of releasing the features and their availability for associated users.
- Change Enablement: This stage assists with increasing the successful IT changes while ensuring that the risks associated with them have been fully addressed and resolved, authorizing the changes to move ahead, and managing the schedule at the same time.
- Service Validation and Testing: This process helps to make informed decisions about service changes and continuation. There are five steps in this process: plan and design tests, verify test designs and plans, prepare test environments, perform tests, evaluate exit criteria, and clean test environments.
- Service Configuration Management: This practice enables the accuracy and reliability of the services' configuration and supporting configuration items (CIs) to be available whenever they are needed. This also includes data on how CIs have been configured and relationships amongst them.
- IT Asset Management: This phase helps organizations to manage all the IT assets' lifecycle including control costs, risk management, IT support decision-making about an apt purchase, re-use of available assets, retirement of old or non-working assets, and other contractual requirements.
Demand management
An ITSM process that helps anticipate and brace for meeting customer demands on time and without any additional or unplanned costs. A part of service strategy, this is a critical process that assists businesses in:
- Creating a plan for the service offerings,
- Establishing the scope,
- Drafting the budget, and
- Creating a strategy for service delivery.
- In short, demand management interfaces across multiple processes to manage the expectations of both customers as well as service providers.
Technical Management Practices

Technology Management Practice works upon 3 domains in order to shift the focus of organizations from tech solutions to IT services. Brief details of the domains are given below.
| Deployment Management | This process ensures that the business changes have minimal impact on the current production environment by taking care of software deployment. Release planning, deployment, build and test release, early life support, and reviewing and closure are the activities in this process. |
| Infrastructure and Platform Management | This practice enables to manage the infrastructure and platforms appropriately that have been used by the organization. It also monitors the reliable technology solutions available at the present to the organization including the technology of external service providers. |
| Software Development and Management | This last stage of technical management practice ensures that applications have met the needs of internal and external stakeholders with respect to compliance, suitability, dependability, functionality, and maintainability. |
Elevate your career with a PMP certification! Acquire project management expertise that distinguishes you in all sectors.
ITIL Processes for Progress
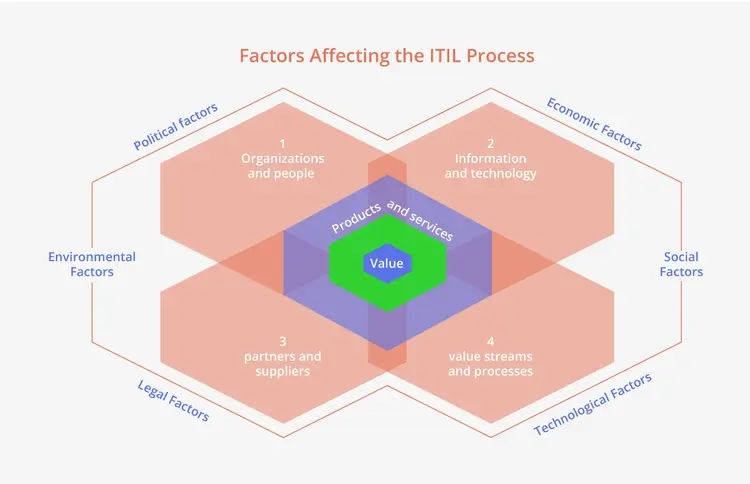
Conclusion
We hope that this article has given you an understanding of the ITIL processes and ITIL service lifecycle stages within each stage. Enroll in the KnowledgeHut ITIL 4 Foundation Certification Course, which is provided by KnowledgeHut, an AXELOS Certified Partner and a PeopleCert® Accredited Training Organization (ATO). This course will give you a thorough understanding of the core concepts and definitions of the ITIL 4 framework.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the ITIL v4 processes?
2. What are the ITIL V3 processes?
3. How many ITIL practices are there?
Get Free Consultation
By submitting, I accept the T&C and
Privacy Policy
Ready to fast-track your ITSM career?
