- Blog Categories
- Project Management
- Agile Management
- IT Service Management
- Cloud Computing
- Business Management
- Business Intelligence
- Quality Engineer
- Cyber Security
- Career
- Big Data
- Programming
- Most Popular Blogs
- PMP Exam Schedule for 2024: Check PMP Exam Date
- Top 60+ PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2024
- PMP Cheat Sheet and PMP Formulas To Use in 2024
- What is PMP Process? A Complete List of 49 Processes of PMP
- Top 15+ Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 170 Project Management Research Topics
- What is Effective Communication: Definition
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel in 2024?
- PMP Certification Exam Eligibility in 2024 [A Complete Checklist]
- PMP Certification Fees - All Aspects of PMP Certification Fee
- Most Popular Blogs
- CSM vs PSM: Which Certification to Choose in 2024?
- How Much Does Scrum Master Certification Cost in 2024?
- CSPO vs PSPO Certification: What to Choose in 2024?
- 8 Best Scrum Master Certifications to Pursue in 2024
- Safe Agilist Exam: A Complete Study Guide 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- SAFe vs Agile: Difference Between Scaled Agile and Agile
- Top 21 Scrum Best Practices for Efficient Agile Workflow
- 30 User Story Examples and Templates to Use in 2024
- State of Agile: Things You Need to Know
- Top 24 Career Benefits of a Certifed Scrum Master
- Most Popular Blogs
- ITIL Certification Cost in 2024 [Exam Fee & Other Expenses]
- Top 17 Required Skills for System Administrator in 2024
- How Effective Is Itil Certification for a Job Switch?
- IT Service Management (ITSM) Role and Responsibilities
- Top 25 Service Based Companies in India in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- What is Escalation Matrix & How Does It Work? [Types, Process]
- ITIL Service Operation: Phases, Functions, Best Practices
- 10 Best Facility Management Software in 2024
- What is Service Request Management in ITIL? Example, Steps, Tips
- An Introduction To ITIL® Exam
- Most Popular Blogs
- A Complete AWS Cheat Sheet: Important Topics Covered
- Top AWS Solution Architect Projects in 2024
- 15 Best Azure Certifications 2024: Which one to Choose?
- Top 22 Cloud Computing Project Ideas in 2024 [Source Code]
- How to Become an Azure Data Engineer? 2024 Roadmap
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 40 IoT Project Ideas and Topics in 2024 [Source Code]
- The Future of AWS: Top Trends & Predictions in 2024
- AWS Solutions Architect vs AWS Developer [Key Differences]
- Top 20 Azure Data Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- 25 Best Cloud Computing Tools in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Company Analysis Report: Examples, Templates, Components
- 400 Trending Business Management Research Topics
- Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK): Guide
- ECBA Certification: Is it Worth it?
- How to Become Business Analyst in 2024? Step-by-Step
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 20 Business Analytics Project in 2024 [With Source Code]
- ECBA Certification Cost Across Countries
- Top 9 Free Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates
- Business Analyst Job Description in 2024 [Key Responsibility]
- Business Analysis Framework: Elements, Process, Techniques
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Career Options after BCom to Know in 2024
- Top 10 Power Bi Books of 2024 [Beginners to Experienced]
- Power BI Skills in Demand: How to Stand Out in the Job Market
- Top 15 Power BI Project Ideas
- Top Picks by Authors
- 10 Limitations of Power BI: You Must Know in 2024
- Top 45 Career Options After BBA in 2024 [With Salary]
- Top Power BI Dashboard Templates of 2024
- What is Power BI Used For - Practical Applications Of Power BI
- SSRS Vs Power BI - What are the Key Differences?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Data Collection Plan For Six Sigma: How to Create One?
- Quality Engineer Resume for 2024 [Examples + Tips]
- 20 Best Quality Management Certifications That Pay Well in 2024
- Six Sigma in Operations Management [A Brief Introduction]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Six Sigma Green Belt vs PMP: What's the Difference
- Quality Management: Definition, Importance, Components
- Adding Green Belt Certifications to Your Resume
- Six Sigma Green Belt in Healthcare: Concepts, Benefits and Examples
- Most Popular Blogs
- Latest CISSP Exam Dumps of 2024 [Free CISSP Dumps]
- CISSP vs Security+ Certifications: Which is Best in 2024?
- Best CISSP Study Guides for 2024 + CISSP Study Plan
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker in 2024?
- Top Picks by Authors
- CISSP vs Master's Degree: Which One to Choose in 2024?
- CISSP Endorsement Process: Requirements & Example
- OSCP vs CISSP | Top Cybersecurity Certifications
- How to Pass the CISSP Exam on Your 1st Attempt in 2024?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Career Options & Courses After 12th Commerce in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- 30 Best Answers for Your 'Reason for Job Change' in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- Time Management Skills: How it Affects your Career
- Most Popular Blogs
- Top 28 Big Data Companies to Know in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Big Data Tools You Need to Know in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Web Development Using PHP And MySQL
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 30 Software Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- More
- Tutorials
- Practise Tests
- Interview Questions
- Free Courses
- Agile & PMP Practice Tests
- Agile Testing
- Agile Scrum Practice Exam
- CAPM Practice Test
- PRINCE2 Foundation Exam
- PMP Practice Exam
- Cloud Related Practice Test
- Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- AWS Solutions Architect
- AWS Developer Associate
- IT Related Pratice Test
- ITIL Practice Test
- Devops Practice Test
- TOGAF® Practice Test
- Other Practice Test
- Oracle Primavera P6 V8
- MS Project Practice Test
- Project Management & Agile
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Release Train Engineer Interview Questions
- Agile Coach Interview Questions
- Scrum Interview Questions
- IT Project Manager Interview Questions
- Cloud & Data
- Azure Databricks Interview Questions
- AWS architect Interview Questions
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Kubernetes Interview Questions
- Web Development
- CSS3 Free Course with Certificates
- Basics of Spring Core and MVC
- Javascript Free Course with Certificate
- React Free Course with Certificate
- Node JS Free Certification Course
- Data Science
- Python Machine Learning Course
- Python for Data Science Free Course
- NLP Free Course with Certificate
- Data Analysis Using SQL
Quality Control: Importance, Types, Methods
Updated on Nov 25, 2024 | 0.1k views
Share:
Table of Contents
In today’s competitive marketplace, maintaining high standards is essential to meet customer expectations. Quality control is not a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing commitment to continuous improvement. It’s about following steps to check, test, and make production processes better. No matter the industry—whether it’s manufacturing, healthcare, or software—QC helps improve efficiency and cut down on waste.
Making a product without the right controls can waste time, cost a lot, and be risky. To mitigate these risks, businesses implement clear quality control measures. These controls ensure the production process stays on track and help fix quality issues.
Quality control helps businesses save money, work better, and keep customers satisfied. It also creates a positive workplace and encourages employees to take pride in their work. In this blog, we’ll cover the basics of quality control, why it matters, and the career options it offers.
What is Quality Control?
According to the quality control definition, the process involves inspecting, testing, and analyzing products or services to identify and rectify any defects or issues. It is the part of quality management that ensures quality requirements are met. It involves inspecting, testing, and monitoring processes to find and fix defects. The goal is to ensure products are reliable, safe, and meet specifications. By implementing effective QC measures, organizations can improve product quality, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Quality control involves creating an environment where everyone strives for perfection. This means training employees, setting quality standards, and using methods to identify quality variations. It is a continuous process that involves inspecting, testing, and monitoring at different stages. Some quality control examples include checking raw materials, monitoring the manufacturing process, and inspecting the final product. Many industries, such as manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, healthcare, medical, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage, rely on quality control. In non-manufacturing businesses, quality testing may include customer service assessments, surveys, questionnaires, inspections, or audits.
Master Right Skills & Boost Your Career
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session
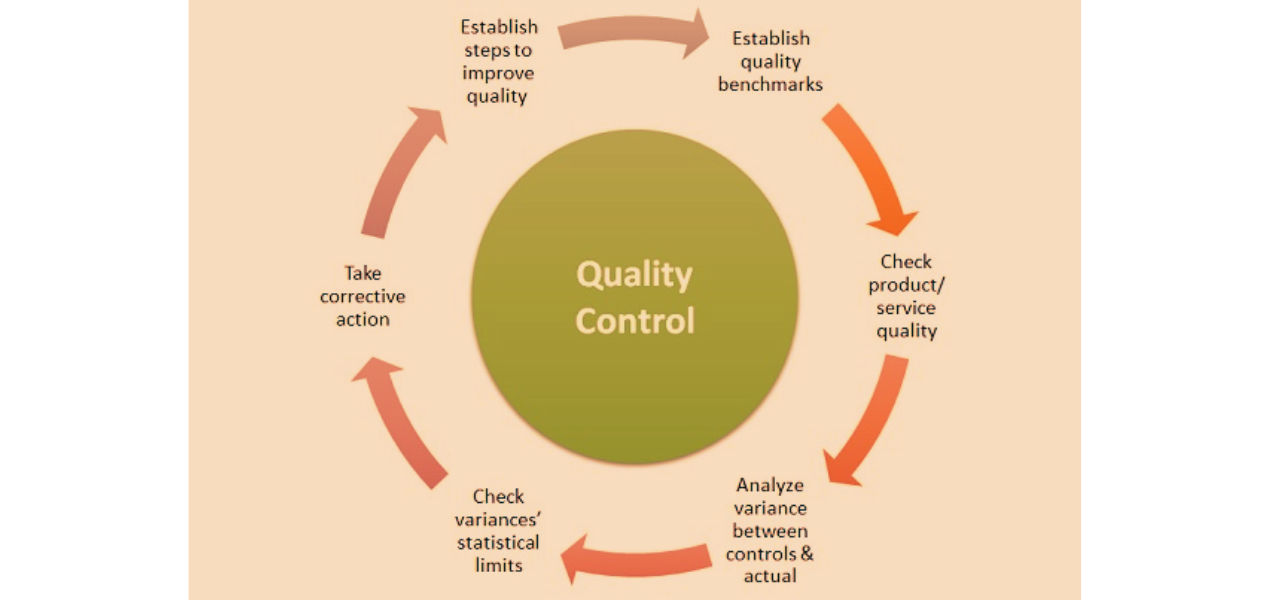
Source: mbaskool
Key Components of Quality Control
Quality control (QC) is a crucial aspect of ensuring products or services meet specified standards. Key components of quality control include:
- Standards and Specifications: Establishing clear guidelines for quality is essential. These standards define the acceptable limits for performance, appearance, and functionality.
- Inspection and Testing: Regular inspections and tests during production help identify defects or deviations from quality standards. This includes physical, chemical, or visual tests depending on the product or service.
- Control Charts: Control charts use statistical tools to monitor process variation and detect trends or abnormalities that could lead to defects.
- Sampling: Since inspecting every item may not be feasible, sampling techniques allow for checking a representative set of products to determine overall quality.
- Documentation and Records: Maintaining detailed records of inspections, tests, and corrective actions for accountability and traceability.
- Root Cause Analysis: Finding the root cause of defects is necessary for their resolution using tools like the "5 Whys." This approach prevents recurring issues.
- Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA): Fixing defects and preventing recurring issues are essential for ongoing improvement.
- Training and Education: Providing employees with the knowledge and skills to maintain quality standards.
- Continuous Improvement: Using data and feedback to identify areas of improvement and enhance the overall quality management system.
Importance of Quality Control
Quality control ensures high standards, customer satisfaction, and a strong brand reputation. QC helps businesses detect defects early, reduce errors, and deliver reliable outputs.
- Brand Reputation: Robust QC builds a strong brand reputation, fostering trust, loyalty, and positive word-of-mouth. When businesses consistently deliver high-quality products or services, they earn the trust of their customers.
- Cost Reduction: Early defect detection prevents costly rework, waste, and recalls. This improves efficiency and saves resources, contributing to the organization’s profitability.
- Customer Loyalty: Quality Control plays a key role in earning customer loyalty. Customers are more likely to stay with a brand when they consistently receive good quality. This leads to repeat business and higher customer value over time.
- Compliance: QC also plays a vital role in compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Adhering to these ensures the safety, reliability, and legality of products and services. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties and loss of credibility.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that prioritize quality gain a significant edge in the market. High-quality products or services help businesses differentiate themselves. They draw in selective customers. And warrant higher prices due to their dependability and excellence.
- Risk Mitigation: Quality Control helps mitigate risks by identifying and addressing issues early. This approach prevents reputational harm, legal issues, and financial losses.
- Continuous Improvement: Quality Control fosters a culture of continuous improvement. This ongoing evaluation boosts efficiency, cuts waste and ensures agility in market changes.
QC in Different Industries
Quality Control (QC) is crucial across various industries to ensure products and services meet the desired standards. While the core principles remain similar, Quality Control techniques can differ based on the specific needs of each industry.
- Manufacturing Industry: In the manufacturing industry, QC focuses on ensuring consistency and reliability in production. Techniques like Statistical Process Control (SPC) and regular inspections are used to minimize defects and optimize production efficiency.
- Food Industry: In the food industry, QC involves rigorous testing to meet health and safety standards. Quality management systems are implemented to ensure product safety and consistency. It involves inspections, monitoring, and hygiene checks to ensure quality.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: In pharmaceuticals, QC is vital for ensuring the safety and efficacy of drugs. Products undergo rigorous testing, including stability and potency checks. This is done to ensure they meet regulatory standards and are safe for consumption.
- Healthcare Industry: In healthcare, QC is implemented for patient safety by following strict protocols. Continuous improvement programs enhance patient care. Regulatory compliance maintains industry standards and accreditations.
- Software Industry: In software development, QC ensures the functionality and usability of applications. It includes testing, bug fixes, and validation to meet user needs and standards.
In all industries, QC is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction, minimizing defects, and improving overall performance.
Types of Quality Control
Quality control (QC) ensures products and services meet standards and customer expectations. To achieve this, organizations implement various types of QC. Let us look at each of these types:
- Preventive Quality Control: This approach focuses on preventing issues before they arise during production. It includes measures like employee training, regular equipment maintenance, and optimizing processes to reduce the risk of defects.
- Corrective Quality Control: Corrective QC identifies and resolves problems during or after production. Techniques like inspections, testing, and monitoring are used to detect defects and address them promptly, even if preventive measures fail.
- Statistical Quality Control (SQC): SQC uses statistical techniques to monitor and regulate processes. By collecting and analyzing data, organizations can spot trends or variations and make necessary adjustments to maintain consistent quality.
- On-Site Quality Control: This involves performing inspections and tests directly at the production site. It ensures that products meet quality standards before being released, which is vital in industries where production conditions directly affect quality.
- Off-Site Quality Control: Off-site QC involves conducting inspections and tests away from the production site, often through third-party labs. This provides an independent and objective evaluation of product quality, enhancing transparency and trust.
Quality Control Methods
Quality control methods are essential for ensuring products and services meet specific standards. Here are some common techniques:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): This method uses statistical techniques to monitor and control processes. By analyzing data from samples, SPC helps identify trends, variations, and potential issues.
- Acceptance Sampling: This involves inspecting a sample of products to determine whether an entire batch meets quality standards. Statistical techniques are used to calculate the probability of acceptance or rejection based on sample results.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA): RCA identifies the underlying reasons for defects, enabling corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
- Process Control: This focuses on monitoring and adjusting processes to maintain
- quality. It involves setting control limits and taking corrective actions when deviations occur.
- Inspection: This involves examining products or services to identify defects or non-conformities. Inspection can be done visually, dimensionally, or functionally.
- Audits: Internal or external audits verify adherence to quality management systems and standards. Regular audits help identify gaps and improve processes.
- Testing: This involves subjecting products or services to various tests to assess their performance, durability, or functionality. Testing can be destructive or non-destructive.
Quality Control Roles and Responsibilities
Quality Control (QC) roles vary across industries, but the core roles and responsibilities often include:
Quality Control Manager: The QC Manager overlooks the entire quality control process. They establish quality standards, develop and implement QC plans, and monitor the effectiveness of QC activities. They also communicate quality expectations across the organization.
Inspector/Tester: Inspectors and testers carry out on-site inspections and tests for quality control. They ensure quality compliance, identify discrepancies, and support quality assurance.
Quality Analyst: Quality analysts analyze data collected from QC activities using statistical tools. They analyze trends and areas for improvement, provide insights to drive decisions and ensure high quality.
Process Improvement Specialist: Process improvement specialists identify ways to enhance efficiency and reduce defects. They work collaboratively with teams to optimize processes and improve overall quality.
Training Coordinator: Training coordinators are responsible for designing and delivering training programs related to quality control. They ensure team members are trained in QC procedures, standards, and methods, building a skilled workforce.
Quality Control Careers
Quality control careers involve ensuring that products and services meet the highest standards. These roles are crucial in maintaining consistency, improving processes, and ensuring customer satisfaction. Let's look at some key quality control job roles and their average salaries:
1. Quality Control Manager:
Quality Control Manager oversees the QC department, ensuring processes align with organizational goals, and manages staff. The average salary of a quality control manager is $120,707. An entry-level quality control manager with 1-3 years of experience earns an average salary of $84,362. In contrast, a senior-level quality control manager with over 8 years of experience earns an average salary of $149,936.
Source: Salary.com
2. Quality Control Specialist:
A Quality Control Specialist is responsible for ensuring that products or services meet established quality standards and regulatory requirements. The average annual salary for a Quality Control Specialist in the United States is $125,783. According to Salary.com, the salary range for Quality Control Specialists in the US can vary from $89,335 to $152,641, with most earning between $106,705 and $139,841.
Source: Salary.com
3. Quality Control Engineer:
A QC Engineer works at a technical level, analyzing and improving production processes. They apply engineering methods to ensure quality and develop quality control systems. Most Quality Control Engineers in the US earn between $80,082 and $94,381 annually, with the average salary coming in at $87,379.
Source: Salary.com
4. Quality Control Technician:
A Quality Control Technician is responsible for testing and inspecting products or services to meet quality standards and specifications. While the average salary for Quality Control Technicians in the US is $57,913, the range can vary significantly. Top earners can make up to $71,074, while some positions start as low as $51,063. The majority of technicians fall within a range of $54,327 to $64,802.
Source: Salary.com
Conclusion
The bottom line is Quality control is essential for delivering top-notch products and services that match customer demands and adhere to regulatory requirements. Understanding the difference between quality control vs quality assurance is essential for businesses aiming to enhance product quality and optimize processes. Quality Control ensures product quality and business success. Organizations can improve product quality, reduce costs, increase customer satisfaction, and stay competitive. It also fosters a positive work environment and a sense of ownership among employees.
Quality control involves training staff, using data-driven tools, and setting standards. It ensures workplace safety and produces products that meet safety and customer requirements. Also, it offers rewarding career opportunities for problem-solvers and process improvers. Embracing QC not only ensures the best outcomes for customers but also creates a thriving, sustainable business environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is QA vs QC controls?
2. What is a QC checklist?
3. What is QC in Six Sigma?
4. What are the QC standards?
5. Which comes first, QA or QC?
Get Free Consultation
By submitting, I accept the T&C and
Privacy Policy
