- Blog Categories
- Project Management
- Agile Management
- IT Service Management
- Cloud Computing
- Business Management
- Business Intelligence
- Quality Engineer
- Cyber Security
- Career
- Big Data
- Programming
- Most Popular Blogs
- PMP Exam Schedule for 2024: Check PMP Exam Date
- Top 60+ PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2024
- PMP Cheat Sheet and PMP Formulas To Use in 2024
- What is PMP Process? A Complete List of 49 Processes of PMP
- Top 15+ Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 170 Project Management Research Topics
- What is Effective Communication: Definition
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel in 2024?
- PMP Certification Exam Eligibility in 2024 [A Complete Checklist]
- PMP Certification Fees - All Aspects of PMP Certification Fee
- Most Popular Blogs
- CSM vs PSM: Which Certification to Choose in 2024?
- How Much Does Scrum Master Certification Cost in 2024?
- CSPO vs PSPO Certification: What to Choose in 2024?
- 8 Best Scrum Master Certifications to Pursue in 2024
- Safe Agilist Exam: A Complete Study Guide 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- SAFe vs Agile: Difference Between Scaled Agile and Agile
- Top 21 Scrum Best Practices for Efficient Agile Workflow
- 30 User Story Examples and Templates to Use in 2024
- State of Agile: Things You Need to Know
- Top 24 Career Benefits of a Certifed Scrum Master
- Most Popular Blogs
- ITIL Certification Cost in 2024 [Exam Fee & Other Expenses]
- Top 17 Required Skills for System Administrator in 2024
- How Effective Is Itil Certification for a Job Switch?
- IT Service Management (ITSM) Role and Responsibilities
- Top 25 Service Based Companies in India in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- What is Escalation Matrix & How Does It Work? [Types, Process]
- ITIL Service Operation: Phases, Functions, Best Practices
- 10 Best Facility Management Software in 2024
- What is Service Request Management in ITIL? Example, Steps, Tips
- An Introduction To ITIL® Exam
- Most Popular Blogs
- A Complete AWS Cheat Sheet: Important Topics Covered
- Top AWS Solution Architect Projects in 2024
- 15 Best Azure Certifications 2024: Which one to Choose?
- Top 22 Cloud Computing Project Ideas in 2024 [Source Code]
- How to Become an Azure Data Engineer? 2024 Roadmap
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 40 IoT Project Ideas and Topics in 2024 [Source Code]
- The Future of AWS: Top Trends & Predictions in 2024
- AWS Solutions Architect vs AWS Developer [Key Differences]
- Top 20 Azure Data Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- 25 Best Cloud Computing Tools in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Company Analysis Report: Examples, Templates, Components
- 400 Trending Business Management Research Topics
- Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK): Guide
- ECBA Certification: Is it Worth it?
- How to Become Business Analyst in 2024? Step-by-Step
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 20 Business Analytics Project in 2024 [With Source Code]
- ECBA Certification Cost Across Countries
- Top 9 Free Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates
- Business Analyst Job Description in 2024 [Key Responsibility]
- Business Analysis Framework: Elements, Process, Techniques
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Career Options after BCom to Know in 2024
- Top 10 Power Bi Books of 2024 [Beginners to Experienced]
- Power BI Skills in Demand: How to Stand Out in the Job Market
- Top 15 Power BI Project Ideas
- Top Picks by Authors
- 10 Limitations of Power BI: You Must Know in 2024
- Top 45 Career Options After BBA in 2024 [With Salary]
- Top Power BI Dashboard Templates of 2024
- What is Power BI Used For - Practical Applications Of Power BI
- SSRS Vs Power BI - What are the Key Differences?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Data Collection Plan For Six Sigma: How to Create One?
- Quality Engineer Resume for 2024 [Examples + Tips]
- 20 Best Quality Management Certifications That Pay Well in 2024
- Six Sigma in Operations Management [A Brief Introduction]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Six Sigma Green Belt vs PMP: What's the Difference
- Quality Management: Definition, Importance, Components
- Adding Green Belt Certifications to Your Resume
- Six Sigma Green Belt in Healthcare: Concepts, Benefits and Examples
- Most Popular Blogs
- Latest CISSP Exam Dumps of 2024 [Free CISSP Dumps]
- CISSP vs Security+ Certifications: Which is Best in 2024?
- Best CISSP Study Guides for 2024 + CISSP Study Plan
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker in 2024?
- Top Picks by Authors
- CISSP vs Master's Degree: Which One to Choose in 2024?
- CISSP Endorsement Process: Requirements & Example
- OSCP vs CISSP | Top Cybersecurity Certifications
- How to Pass the CISSP Exam on Your 1st Attempt in 2024?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Career Options & Courses After 12th Commerce in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- 30 Best Answers for Your 'Reason for Job Change' in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- Time Management Skills: How it Affects your Career
- Most Popular Blogs
- Top 28 Big Data Companies to Know in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Big Data Tools You Need to Know in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Web Development Using PHP And MySQL
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 30 Software Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- More
- Tutorials
- Practise Tests
- Interview Questions
- Free Courses
- Agile & PMP Practice Tests
- Agile Testing
- Agile Scrum Practice Exam
- CAPM Practice Test
- PRINCE2 Foundation Exam
- PMP Practice Exam
- Cloud Related Practice Test
- Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- AWS Solutions Architect
- AWS Developer Associate
- IT Related Pratice Test
- ITIL Practice Test
- Devops Practice Test
- TOGAF® Practice Test
- Other Practice Test
- Oracle Primavera P6 V8
- MS Project Practice Test
- Project Management & Agile
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Release Train Engineer Interview Questions
- Agile Coach Interview Questions
- Scrum Interview Questions
- IT Project Manager Interview Questions
- Cloud & Data
- Azure Databricks Interview Questions
- AWS architect Interview Questions
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Kubernetes Interview Questions
- Web Development
- CSS3 Free Course with Certificates
- Basics of Spring Core and MVC
- Javascript Free Course with Certificate
- React Free Course with Certificate
- Node JS Free Certification Course
- Data Science
- Python Machine Learning Course
- Python for Data Science Free Course
- NLP Free Course with Certificate
- Data Analysis Using SQL
What are Kubernetes Pods? Types, Examples, Best Practices
By Mayank Modi
Updated on Nov 05, 2022 | 9 min read | 14.0k views
Share:
Table of Contents
Kubernetes (sometimes shortened to K8s with the 8 standing for the number of letters between the “K” and the “s”) is an open-source system to deploy, scale, and manage containerized applications anywhere. Kubernetes is a container-centric management software that allows the creation and deployment of containerized applications with ease. In Kubernetes, Pods are the fundamental building blocks. They are the smallest deployable units that can create and manage.
Originally created by Google Cloud in 2014, Kubernetes is now being offered by leading Cloud Providers like AWS and Azure. In this article, we are going to have a look into the working of Kubernetes and the creation of Kubernetes Pods for the deployment of applications.
What are Kubernetes Pods?
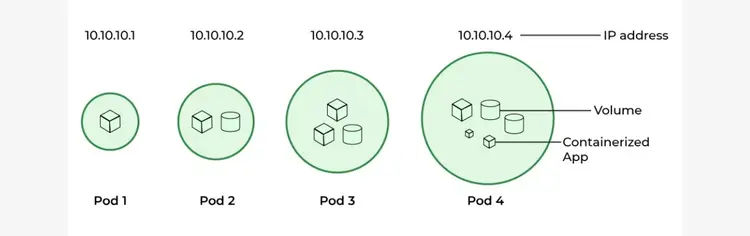
Pods are the smallest execution unit in Kubernetes. As the official Documentation says “A Pod (as in a pod of whales or pea pod) is a group of one or more containers, with shared storage and network resources, and a specification for how to run the containers.”
For example, Let's assume that we have 5 containers ready for Kubernetes deployment. We can put all 5 containers in the same pod if all of them have to be run with the same configuration or we can divide the containers based on their purpose and load management.
Pods can also persist volumes just like docker, and they can be easily configured based on the requirement. Each Pod is tied to the Node where it is scheduled and remains there until termination (according to restart policy) or deletion. In case of a Node failure, identical Pods are scheduled on other available Nodes in the cluster.
If you're looking to learn about the basic of Kubernetes, you can refer our video on Kubernetes Architecture.
Types of Kubernetes Pods
There are two types of pods in Kubernetes namely single container pod and multi container pod.
1. Single Container Pod
As the name suggests, if there is only a single container running in the Kubernetes pod, then it is called a single container pod and it can easily be created with the help of a YAML file. Here is a sample YAML file used to create a pod with the postgres database.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: Postgres
spec:
containers:
- name: Postgres
image: Postgres: 3.1
ports:
containerPort: 8000
imagePullPolicy: Always 2. Multi Container Pod
In this type of pod, we can run multiple containers within a single pod. It can be created by specifying the containers in the same YAML file. Here is a sample YAML file used to create a multi container Pod with Tomcat and MongoDB images.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: Tomcat
spec:
containers:
- name: Tomcat
image: tomcat: 8.0
ports:
containerPort: 7500
imagePullPolicy: Always
-name: Database
Image: mongoDB
Ports:
containerPort: 7501
imagePullPolicy: Always Other than the number of containers running in the pod, there is no difference between a single-container pod and a multi-container pod.
How to Create a Pods in Kubernetes?
In order to create a pod, we need to create a Kubernetes cluster in which we can have multiple pods based on the requirement. The clusters can also be scaled horizontally as well as vertically based on the workload. There is also an option of autoscaling based on the incoming load. Clusters are basically a set of nodes that run docker applications.
The application needs to dockerized with its own set of requirements and necessary services to keep it running. When compared to virtual machines, these are much more flexible and lightweight.
Clusters should at least have a master node, and they can have any number of worker nodes. The master node controls the entire cluster and monitors the activity, logs and metrics related to the cluster. To create a Kubernetes pod, we must create a Kubernetes cluster with the necessary configurations. A pod can be created on top of the Kubernetes cluster only. To create a pod, we must configure the yaml file according to the requirements. Here is a sample yaml file.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80 - Apiversion: This field can be used to denote the version of the service that is being deployed in Kubernetes.
- Kind: This is usually the kind of deployment in Kubernetes. In this case, the container is being deployed in a pod.
- Metadata: This field is used to configure other metadata of the container that is being deployed in K8s.
- Spec: This field is used to configure the settings of pod and the port that should be used to deploy the service in K8s.
Command :
kubectl create -f manifests/rs-example.yaml The main difference between create and apply commands in K8s is that create is used as a declarative state like defining the pod whereas create command in K8s is used to implement the state that has been declared.
Creates the pod with the above configurations mentioned in the YAML file.
To check if the Pod is running in the Kubernetes cluster:
Command:
kubectl get pods --watch --show-labels Learn more about DevOps and writing pipelines with the Best DevOps Courses Online.
How to View a Kubernetes Pod?
To view all the pods running in a Kubernetes cluster, we can use the following command:
Command
kubectl get pods This command will list all the pods running in a particular Kubernetes cluster.
To get the pod configuration we can use the following command
Command
kubectl describe pod This command will list the nginxconfiguration along with the pod configuration details.
How to Implement Kubernetes Pod Policy?
A Pod Security Policy defines a set of conditions a pod must run with in order to run on the cluster. These conditions span host-level access, to a range of UIDs a container can run as, and even what volumes a pod can use.
All the policies are configurable in the yaml file used to create a pod. The Yaml file can be used to implement various rules and policies over the Kubernetes pod.
Here is a sample yaml file which implements policies over the pod.
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodSecurityPolicy
metadata:
name: my-restricted-psp
spec:
privileged: false
# Required to prevent escalations to root.
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
# Allow core volume types.
volumes:
- 'configMap'
- 'emptyDir'
- 'projected'
- 'secret'
- 'downwardAPI'
- 'nfs'
- 'persistentVolumeClaim'
- 'awsElasticBlockStore'
hostNetwork: false
hostIPC: false
hostPID: false
runAsUser:
# Require the container to run without root privileges.
rule: 'RunAsAny'
seLinux:
# This policy assumes the nodes are using AppArmor rather than SELinux.
rule: 'RunAsAny'
supplementalGroups:
rule: 'MustRunAs'
ranges:
# Forbid adding the root group.
- min: 1
max: 65535
fsGroup:
rule: 'MustRunAs'
ranges:
# Forbid adding the root group.
- min: 1
max: 65535
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false To see what security policy your pod is using, you can type in the following command in the terminal.
kubectl describe <pod-name> -n <your-namespace> You can refer to the following documentation for the types of policies that can be implemented over a Kubernetes pod.
How to Destroy Kubernetes Pod?
It is also important to delete or kill the pods which are not used anymore in the Kubernetes cluster. The following command kills the pod present in the Kubernetes cluster.
Command
kubectl delete pod <pod-name> After executing the above command, you will get pod <pod-name> deleted. This confirms that the pod has been successfully deleted in the Kubernetes cluster.
Labels
Labels are usually key value pairs that are attached in the yaml file to identify and indicate to the end user that this pod hosts certain kind of service. Its usually in the meta data section of the yaml file.
"metadata": {
"labels": {
"key1" : "value1",
"key2" : "value2"
}
} Kubernetes Pods Best Practices for Security, Reliability and Resource Requests
It is important to know some of the best practices that engineers follow when it comes to Kubernetes.
- Understand and embrace the ephemeral nature of Kubernetes.
- Avoid single points of failure.
- Set resource requests and limits for CPU and memory.
- Use liveness and readiness probes.
It is also necessary to configure the pods according to the requirement to save costs if its running in a managed instance and to optimize computations.
To read more about Kubernetes and deployment, you can refer to the best Kubernetes course online.
Conclusion
Kubernetes Pods are the essential building blocks of containerized applications in Kubernetes. In this blog, we have discussed the basics of Kubernetes and stepping slowly to understand Kubernetes pods, the steps to create a pod as well as to monitor pods in a Kubernetes cluster. We have also covered some of the best practices of Kubernetes followed in the DevOps world.
Enrolling to the Best Docker and Kubernetes Course at the right time can boost your DevOps career. You can also refer to the following resources to know more about K8s.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How many ways can we create pods in Kubernetes?
2. What is the difference between POD and container?
3. What is the difference between POD and node?
4. Can we run two containers in a pod?
Get Free Consultation
By submitting, I accept the T&C and
Privacy Policy
