- Blog Categories
- Project Management
- Agile Management
- IT Service Management
- Cloud Computing
- Business Management
- Business Intelligence
- Quality Engineer
- Cyber Security
- Career
- Big Data
- Programming
- Most Popular Blogs
- PMP Exam Schedule for 2024: Check PMP Exam Date
- Top 60+ PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2024
- PMP Cheat Sheet and PMP Formulas To Use in 2024
- What is PMP Process? A Complete List of 49 Processes of PMP
- Top 15+ Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 170 Project Management Research Topics
- What is Effective Communication: Definition
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel in 2024?
- PMP Certification Exam Eligibility in 2024 [A Complete Checklist]
- PMP Certification Fees - All Aspects of PMP Certification Fee
- Most Popular Blogs
- CSM vs PSM: Which Certification to Choose in 2024?
- How Much Does Scrum Master Certification Cost in 2024?
- CSPO vs PSPO Certification: What to Choose in 2024?
- 8 Best Scrum Master Certifications to Pursue in 2024
- Safe Agilist Exam: A Complete Study Guide 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- SAFe vs Agile: Difference Between Scaled Agile and Agile
- Top 21 Scrum Best Practices for Efficient Agile Workflow
- 30 User Story Examples and Templates to Use in 2024
- State of Agile: Things You Need to Know
- Top 24 Career Benefits of a Certifed Scrum Master
- Most Popular Blogs
- ITIL Certification Cost in 2024 [Exam Fee & Other Expenses]
- Top 17 Required Skills for System Administrator in 2024
- How Effective Is Itil Certification for a Job Switch?
- IT Service Management (ITSM) Role and Responsibilities
- Top 25 Service Based Companies in India in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- What is Escalation Matrix & How Does It Work? [Types, Process]
- ITIL Service Operation: Phases, Functions, Best Practices
- 10 Best Facility Management Software in 2024
- What is Service Request Management in ITIL? Example, Steps, Tips
- An Introduction To ITIL® Exam
- Most Popular Blogs
- A Complete AWS Cheat Sheet: Important Topics Covered
- Top AWS Solution Architect Projects in 2024
- 15 Best Azure Certifications 2024: Which one to Choose?
- Top 22 Cloud Computing Project Ideas in 2024 [Source Code]
- How to Become an Azure Data Engineer? 2024 Roadmap
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 40 IoT Project Ideas and Topics in 2024 [Source Code]
- The Future of AWS: Top Trends & Predictions in 2024
- AWS Solutions Architect vs AWS Developer [Key Differences]
- Top 20 Azure Data Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- 25 Best Cloud Computing Tools in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Company Analysis Report: Examples, Templates, Components
- 400 Trending Business Management Research Topics
- Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK): Guide
- ECBA Certification: Is it Worth it?
- How to Become Business Analyst in 2024? Step-by-Step
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 20 Business Analytics Project in 2024 [With Source Code]
- ECBA Certification Cost Across Countries
- Top 9 Free Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates
- Business Analyst Job Description in 2024 [Key Responsibility]
- Business Analysis Framework: Elements, Process, Techniques
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Career Options after BCom to Know in 2024
- Top 10 Power Bi Books of 2024 [Beginners to Experienced]
- Power BI Skills in Demand: How to Stand Out in the Job Market
- Top 15 Power BI Project Ideas
- Top Picks by Authors
- 10 Limitations of Power BI: You Must Know in 2024
- Top 45 Career Options After BBA in 2024 [With Salary]
- Top Power BI Dashboard Templates of 2024
- What is Power BI Used For - Practical Applications Of Power BI
- SSRS Vs Power BI - What are the Key Differences?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Data Collection Plan For Six Sigma: How to Create One?
- Quality Engineer Resume for 2024 [Examples + Tips]
- 20 Best Quality Management Certifications That Pay Well in 2024
- Six Sigma in Operations Management [A Brief Introduction]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Six Sigma Green Belt vs PMP: What's the Difference
- Quality Management: Definition, Importance, Components
- Adding Green Belt Certifications to Your Resume
- Six Sigma Green Belt in Healthcare: Concepts, Benefits and Examples
- Most Popular Blogs
- Latest CISSP Exam Dumps of 2024 [Free CISSP Dumps]
- CISSP vs Security+ Certifications: Which is Best in 2024?
- Best CISSP Study Guides for 2024 + CISSP Study Plan
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker in 2024?
- Top Picks by Authors
- CISSP vs Master's Degree: Which One to Choose in 2024?
- CISSP Endorsement Process: Requirements & Example
- OSCP vs CISSP | Top Cybersecurity Certifications
- How to Pass the CISSP Exam on Your 1st Attempt in 2024?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Career Options & Courses After 12th Commerce in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- 30 Best Answers for Your 'Reason for Job Change' in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- Time Management Skills: How it Affects your Career
- Most Popular Blogs
- Top 28 Big Data Companies to Know in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Big Data Tools You Need to Know in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Web Development Using PHP And MySQL
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 30 Software Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- More
- Tutorials
- Practise Tests
- Interview Questions
- Free Courses
- Agile & PMP Practice Tests
- Agile Testing
- Agile Scrum Practice Exam
- CAPM Practice Test
- PRINCE2 Foundation Exam
- PMP Practice Exam
- Cloud Related Practice Test
- Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- AWS Solutions Architect
- AWS Developer Associate
- IT Related Pratice Test
- ITIL Practice Test
- Devops Practice Test
- TOGAF® Practice Test
- Other Practice Test
- Oracle Primavera P6 V8
- MS Project Practice Test
- Project Management & Agile
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Release Train Engineer Interview Questions
- Agile Coach Interview Questions
- Scrum Interview Questions
- IT Project Manager Interview Questions
- Cloud & Data
- Azure Databricks Interview Questions
- AWS architect Interview Questions
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Kubernetes Interview Questions
- Web Development
- CSS3 Free Course with Certificates
- Basics of Spring Core and MVC
- Javascript Free Course with Certificate
- React Free Course with Certificate
- Node JS Free Certification Course
- Data Science
- Python Machine Learning Course
- Python for Data Science Free Course
- NLP Free Course with Certificate
- Data Analysis Using SQL
How to Prevent Cyber Attacks in 2025? [10 Effective Steps]
Updated on Oct 21, 2022 | 14 min read | 14.3k views
Share:
Table of Contents
Did you know that the global cost of cyber-attacks is expected to grow 15% every year and by $10 trillion (as per cybersecurityventures.com)? So, how well are the organizations prepared for this? It is known that organizations with an incident response plan reduced data breach cost by 61%. At the same time, 11% of breaches happened due to Ransomware attacks.
In a survey by Yahoo Finance, around 78% of respondents claim that their business's security needs modifications. However, approximately 43% of businesses don't have cyber defenses. It is possible to train your cybersecurity experts using courses on Cyber Security and fight these cyber threats effectively. In this article, we will discuss more about how to prevent a cyber-attack and how you can remain secure as a business.
What are Cyber Attacks?
A cyber-attack is a different set of actions performed by threat actors trying to breach another organization's information system. The individual or group of individuals who use different tactics, techniques, and procedures performs the attacks. People who do perform these threats are usually called cybercriminals, bad actors, hackers, or threat actors. They identify vulnerabilities, problems, or weaknesses in a computer system.
How to Prevent Cyber Attacks Effectively? [In 10 Steps]
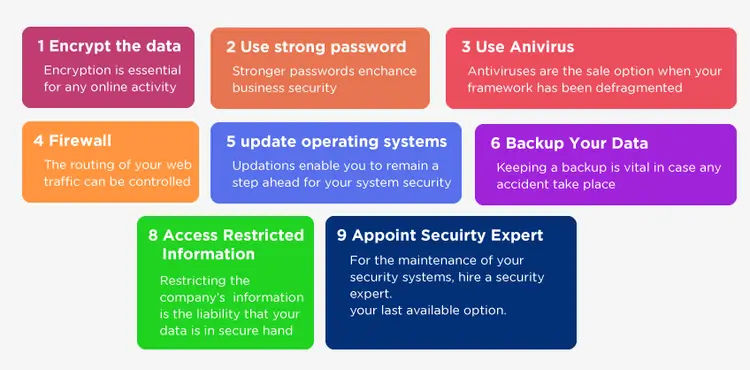
To identify cyber-attack solutions, follow the below-mentioned steps:
Step 1: Incorporate Zero Trust Inspection
The idea of verifying everything and not trusting anyone has become the most important part of cybersecurity efforts. This is the reason why companies are focusing more on encryption and multi-factor authentication. However, some businesses have misunderstood zero trust as a feature or product. Instead, it is a way of using a risk-based approach to Mao the likelihood, frequency, and impact of any particular event and prioritize the highest-value threats.
Step 2: Outsource Protection Needs to a Cybersecurity Firm
Cybersecurity can be quite challenging for businesses, especially for the ones that have limited budgets. Outsourcing cybersecurity to expert companies can bring skilled and dedicated IT experts to keep a check on your network, deal with various types of attacks and check online threat exposure. You must also focus on your businesses, knowing that professionals are up to date for dealing with cyber-attacks.
Step 3: Encrypt Data When Sharing or Uploading Online
Another best method of preventing cyber criminals from intercepting the data during transfers is by encrypting it or using a cloud storage service that provides end-to-end encryption. Also, if you are using the software to encrypt the data before storing it online, keep the decryption key safe. Else, you will lose the data.
For cyber threat prevention, you must use a VPN or encrypt your network through the control panel settings to ensure that your data transfers and online interactions are safe and secure. Companies can collect and store the required information used by cybercriminals, thereby compromising the business data.
Master Right Skills & Boost Your Career
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session
Step 4: Teach Employees About Online Safety
Remote working has exposed many non-tech-savvy employees to cybersecurity threats. The unsecured Wi-Fi networks and work-from-home policies have made collaboration vulnerable. Employees can upskill and learn best practices by enrolling in KnowledgeHut’s IT Security courses, thereby preventing unauthorized access to databases.
Companies must create a workplace culture that understands the importance of cyber security. It is essential to understand the steps on how to prevent cybercrime and be ready with the cyber incident response plan to empower employees to handle all data breaches and threats. They should be trained to keep a check on which sensitive information to send or ignore.
Step 5: Create Complex Passwords or Use Passphrases
Employees often have trouble remembering the user credentials and this is the reason they use simple credentials. But bad and insecure passwords may expose them to huge risks, making it possible for hackers to steal credentials. As a result, companies must focus on passwordless and UEBA (User and Entity Behavior Analytics) strategies for user account security. These modern techniques and technologies not just increase security but also improve user experience.
Step 6: Set Online Safety Guidelines
No matter how many secure infrastructures you apply in your office, every network still has vulnerabilities that may get targeted by hackers. Therefore, businesses need to set some online safety guidelines by upgrading their incident response plan and putting things into practice. IT staff and security companies know their responsibilities, roles, and tasks when a security breach occurs. Additionally, whether is ransomware or some other breach, a quick response could make a huge difference.
Step 7: Protect Employee Information and Store Data Securely
Hackers often use social engineering to manipulate people and steal confidential information. Therefore, companies should limit the amount of information they share online about their employees and businesses. Unsafe data is an open invitation to cybercriminals to come and take advantage. Businesses should store their data securely and can have different data backups to protect sensitive data from theft, loss, destruction, and natural disaster. You can also use encryption before storing it online. Businesses often collect and store personally identifiable information and are a constant attraction to cybercriminals.
Step 8: Establish Mutual Cybersecurity Policies with Business Partners
It is important to have stringent policies that adhere to your business; therefore, coordinating the online safety measures can eliminate the risk of any loopholes, thereby ensuring that your business is completely secured.
Access the backup files and download them to check the recovery process. Identify the vulnerabilities and resolve them to ensure your backed-up files don’t get corrupted. Keep performing other maintenance tasks like destroying unused files or taking help from IT Security courses to know better about mutual cybersecurity policies.
Step 9: Perform a Regular Audit of Cyber Protection Procedures
Although automation is not the solution to every cyber security problem, AI and Machine Learning-powered tools make it easier to set security monitoring. Some businesses also believe that cloud security automation is one of the cost-effective and time-consuming ways to secure your distributed networks.
Also, using automation in cloud investing helps reduce the amount of time, resources, and money that is required to investigate the root cause, scope, and impact of the incident. Additionally, with the amount of data that is stored in the cloud today, companies need the ability to automatically capture and process data at the cloud's speed and scale.
Security teams should not have to worry about working with various cloud teams and access requirements.
Step 10: Install Top Security Antivirus Software and Endpoint Protection
It costs a lot more to lose data than to protect it by investing in high-quality cyber security software. Antivirus software will create a firewall to protect your network from viruses and will restrict the forced attempt to access your system. They will also access your devices and disks to prevent malicious attacks from breaching your business. To know better, you can opt for certified Ethical Hacker training and help prevent your business from getting hacked.
Tips to Protect Cyber Attack
1. Make a Backup of your Data
Always ensure that you must have a backup of your work and confidential files. If the attack happens, you should not fall into data loss. Data loss not just affects a business financially but also affects the reputation of the business.
2. keep track of Who Access your System
Giving access to any random person of your personal devices may put you in unprecedented situations. So, make sure who checks your device in your absence. Put system locks and give credentials only to the respective person.
3. Wi-Fi Protection
Keep your data secure by installing a dedicated Wi-Fi at the workplace. Wi-Fi, compared to LAN, is less secure and should be encrypted properly.
4. Personal Accounts for Employees
Give dedicated personal accounts to every employee to strengthen privacy and confidentiality.
5. Separate Username and Passwords
Don’t use similar usernames and passwords for all your accounts. Keep different passwords and keep on changing them over time. Keeping similar passwords will make your business more vulnerable to lose, and if any malicious activity happens, you may end up losing everything at once.
6. Create Manual Cybersecurity Policies
While there will be policies for protecting devices and systems, stringent rules are also required to keep alert with the attack.
7. Set Online Safety Guidelines
Every business needs a security policy that outlines its guidelines for protecting the company, accessing the internet, and shielding employees from exploitation. For this, companies must set up a secure system for making transactions and protecting the customer's identity and tackling financial losses.
Additionally, threats come not only from cybercriminals but also from business partners, former or current employees, poor internal cybersecurity measures, and more.
Types of Cyber Attacks
There are various different types of attacks that happen, so if you want to know about different types of attacks and their cyber-attacks preventions steps, let us look below:
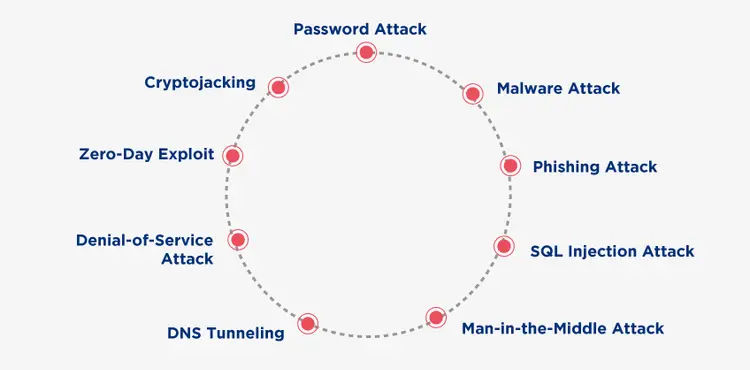
Let us discuss some of the different types of cybercriminals:
1. Password Attack
Password attack is a form of attack when the hacker hacks your password with password-cracking tools like Cain, Abel, Aircrack, Hashcat, etc. Let us see what you can do for the prevention of cyber-attacks:
- Don’t use the same password for different websites or accounts.
- Use strong alphanumeric passwords or special characters.
- Don’t put any password hints open.
- Use the password till the limit.
2. Malware Attack
Malware is one of the most common types of cyberattacks, which refer to malicious software viruses, including spyware, ransomware, adware, Trojans, and more.
Malware breaches a network through vulnerabilities; when the user clicks on the dangerous link, it downloads the attachment, and the attack happens. Let us see how to stop a cyber-attack or prevent a malware attack:
- Use antivirus software to protect your computer against malware.
- Use firewalls to filter the traffic that may enter your device.
- Stay alert and avoid clicking on a suspicious link.
- Update your operating system.
3. Phishing Attack
Phishing is one of the most prominent types of cyberattacks, where the attacker tries to be a trusted contact and sends the victim a fake email.
Not aware of this attack, the victim accidentally opens the mail and clicks on the infected link or the attachment. This way, the attacker gets all access to confidential information.
Some of the ways how to avoid cyber-attacks or minimize the phishing attack are:
- Make use of anti-phishing tools
- Scrutinize the emails.
- Keep updating the passwords.
4. SQL Injection Attack
A SQL injection attack occurs on data-driven websites when the hackers manipulate the standard query. It is carried out by putting the malicious code into the vulnerable search box of the website. This way, the attacker will be able to view, edit and delete the tables in the database. Let us see how to protect from cyber-attacks and keep your business secure:
Use the intrusion detection system to detect unauthorized access to the network.
5. Man-in-the-Middle Attack
The MITM, also called an eavesdropping attack, comes in two-party communication. This means that the attacker hacks the communication between the client and host. This way, hackers can steal and manipulate the client’s data.
MIMT can be prevented by the following mentioned tips, let us understand some of the ways to prevent a cyber-attack:
- Don’t use public Wi-Fi networks.
- Be mindful of the security websites you are using.
- Use encryption on your devices.
6. DNS Tunneling
DNS tunneling is a type of cyber-attack that attack the data of other programs or protocol the DNS queries and responses. This attack includes payloads and is more like a phonebook for the Internet. To stay protected from DNS tunneling:
Use the protocol object and block the DNS tunnel protocol.
7. Denial-of-Service Attack
Denial-of-Service Attack is one of the most significant threats to companies. In this, the hackers target the network or servers and flood them with huge traffic to reduce their bandwidth and exhaust their resources.
When the attack happens, catering to the income requests becomes difficult for the servers, which may affect the website speed, or it may shut a down. For protection against cyber-attacks, you must:
- Do a traffic analysis to identify the inappropriate traffic.
- Check the warning signs like intermittent website shutdown, network slowdown, etc.
- Create an incident response plan and have a checklist.
- Outsource DDoS prevention to cloud-based service providers.
8. Zero-Day Exploit
A Zero Day Exploit happens when the network becomes vulnerable and there’s no solution to prevent the vulnerability. In this, the vendor sends the notification so that the user becomes aware. Depending upon the type of vulnerability, the time taken to fix the attack may vary. Meanwhile, the hacker targets the affected vulnerability and ensures that they exploit the hack before the solution is implemented. To defend against cyber-attack, you should be:
- Following an incident response plan to help you deal with cyber-attack.
- Following a well-communicated patch management process
9. Cryptojacking
The term cryptojacking is related to cryptocurrency; it occurs when the attacker hacks someone else’s device to mine the cryptocurrency. The access is gained by affecting the website or by manipulating the victim to click on the infected link. Sometimes, the attacker also uses online ads with JavaScript code to attack.
For cryptojacking, let us understand how to prevent a cyber-attack on businesses:
- Keep your software updated and have a regular check on security apps.
- Give employees a crypotojacking awareness training.
- Install ad blocker.
10. Social Engineering
Social engineering attack involve human activities, like manipulating people for breaking the normal security procedures and practices to get unauthorized access to the network, system or for any financial gain. Hackers use social engineering attack to hide their true objectives and motives showing themselves as fake trusted sources. Thereby, influencing people and manipulating users to release sensitive information.
Most Noticeable Cyber Attacks in Recent History
Let us look at some of the cyber-attack examples that have impacted globally:
1. Kaseya Ransomware Attack
Kaseya (a US-based provider of remote management software, has experienced a supply chain attack. The whole scenario was made public on July 2, 2021, and was reported to be highly sophisticated.
There was a credentials leak happen, a business logic flaw, a fake software update, and more. The attack was carried out by a Russian-based REvil cybercriminal group. Sometime after the attack, the reports claim that around 800-1500 SMBs were infected.
2. SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack
This was a huge chain attack detected in December 2020 and was named after the victim, SolarWinds. The attack compromised the update meant for SolarWinds’s software platform, Orion.
This was one of the most serious attacks on the United States because it had breached the US military and many of Us based federal agencies.
3. Amazon DDoS Attack
Amazon Web Service, AWS, was the target of a large-scale DDoS attack. The company experienced a 2.3 Tbps DDoS attack, which had a packet forwarding rate of 293.1 Mpps.
4. Twitter Celebrities Attack
Twitter was breached by a group of three attackers who used social engineering attacks to steal the credentials and get access to the company’s internal management system. In this, dozens of popular accounts were hacked, including Jeff Bezos, Barack Obama, and Elon Musk.
Conclusion
Despite the prevalence of Cyber-attacks, a cyber-attack is preventable. However, the key to protection is using end-to-end cyber security architecture that has multi-layers and can be used on all networks. In addition, you must checklist these key points:
- Choose a prevention detection plan.
- Keep security upgrades updated.
- Check all the loopholes.
- Implement advanced technologies.
- Keep threat intelligence up to date.
KnowledgeHut gets you a CyberSAFE Certification course to further enhance and equip your cybersecurity knowledge and prevent security risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Is the Difference Between a Cyberattack and a Cyber Crime?
2. What is the best defense against a cyber-attack?
3. What do you do in case of a cyber-attack?
4. What is the biggest threat to cyber security?
5. What is the most recent cyber attack?
Get Free Consultation
By submitting, I accept the T&C and
Privacy Policy
