- Blog Categories
- Project Management
- Agile Management
- IT Service Management
- Cloud Computing
- Business Management
- Business Intelligence
- Quality Engineer
- Cyber Security
- Career
- Big Data
- Programming
- Most Popular Blogs
- PMP Exam Schedule for 2024: Check PMP Exam Date
- Top 60+ PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2024
- PMP Cheat Sheet and PMP Formulas To Use in 2024
- What is PMP Process? A Complete List of 49 Processes of PMP
- Top 15+ Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 170 Project Management Research Topics
- What is Effective Communication: Definition
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel in 2024?
- PMP Certification Exam Eligibility in 2024 [A Complete Checklist]
- PMP Certification Fees - All Aspects of PMP Certification Fee
- Most Popular Blogs
- CSM vs PSM: Which Certification to Choose in 2024?
- How Much Does Scrum Master Certification Cost in 2024?
- CSPO vs PSPO Certification: What to Choose in 2024?
- 8 Best Scrum Master Certifications to Pursue in 2024
- Safe Agilist Exam: A Complete Study Guide 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- SAFe vs Agile: Difference Between Scaled Agile and Agile
- Top 21 Scrum Best Practices for Efficient Agile Workflow
- 30 User Story Examples and Templates to Use in 2024
- State of Agile: Things You Need to Know
- Top 24 Career Benefits of a Certifed Scrum Master
- Most Popular Blogs
- ITIL Certification Cost in 2024 [Exam Fee & Other Expenses]
- Top 17 Required Skills for System Administrator in 2024
- How Effective Is Itil Certification for a Job Switch?
- IT Service Management (ITSM) Role and Responsibilities
- Top 25 Service Based Companies in India in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- What is Escalation Matrix & How Does It Work? [Types, Process]
- ITIL Service Operation: Phases, Functions, Best Practices
- 10 Best Facility Management Software in 2024
- What is Service Request Management in ITIL? Example, Steps, Tips
- An Introduction To ITIL® Exam
- Most Popular Blogs
- A Complete AWS Cheat Sheet: Important Topics Covered
- Top AWS Solution Architect Projects in 2024
- 15 Best Azure Certifications 2024: Which one to Choose?
- Top 22 Cloud Computing Project Ideas in 2024 [Source Code]
- How to Become an Azure Data Engineer? 2024 Roadmap
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 40 IoT Project Ideas and Topics in 2024 [Source Code]
- The Future of AWS: Top Trends & Predictions in 2024
- AWS Solutions Architect vs AWS Developer [Key Differences]
- Top 20 Azure Data Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- 25 Best Cloud Computing Tools in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Company Analysis Report: Examples, Templates, Components
- 400 Trending Business Management Research Topics
- Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK): Guide
- ECBA Certification: Is it Worth it?
- How to Become Business Analyst in 2024? Step-by-Step
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 20 Business Analytics Project in 2024 [With Source Code]
- ECBA Certification Cost Across Countries
- Top 9 Free Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates
- Business Analyst Job Description in 2024 [Key Responsibility]
- Business Analysis Framework: Elements, Process, Techniques
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Career Options after BCom to Know in 2024
- Top 10 Power Bi Books of 2024 [Beginners to Experienced]
- Power BI Skills in Demand: How to Stand Out in the Job Market
- Top 15 Power BI Project Ideas
- Top Picks by Authors
- 10 Limitations of Power BI: You Must Know in 2024
- Top 45 Career Options After BBA in 2024 [With Salary]
- Top Power BI Dashboard Templates of 2024
- What is Power BI Used For - Practical Applications Of Power BI
- SSRS Vs Power BI - What are the Key Differences?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Data Collection Plan For Six Sigma: How to Create One?
- Quality Engineer Resume for 2024 [Examples + Tips]
- 20 Best Quality Management Certifications That Pay Well in 2024
- Six Sigma in Operations Management [A Brief Introduction]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Six Sigma Green Belt vs PMP: What's the Difference
- Quality Management: Definition, Importance, Components
- Adding Green Belt Certifications to Your Resume
- Six Sigma Green Belt in Healthcare: Concepts, Benefits and Examples
- Most Popular Blogs
- Latest CISSP Exam Dumps of 2024 [Free CISSP Dumps]
- CISSP vs Security+ Certifications: Which is Best in 2024?
- Best CISSP Study Guides for 2024 + CISSP Study Plan
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker in 2024?
- Top Picks by Authors
- CISSP vs Master's Degree: Which One to Choose in 2024?
- CISSP Endorsement Process: Requirements & Example
- OSCP vs CISSP | Top Cybersecurity Certifications
- How to Pass the CISSP Exam on Your 1st Attempt in 2024?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Career Options & Courses After 12th Commerce in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- 30 Best Answers for Your 'Reason for Job Change' in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- Time Management Skills: How it Affects your Career
- Most Popular Blogs
- Top 28 Big Data Companies to Know in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Big Data Tools You Need to Know in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Web Development Using PHP And MySQL
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 30 Software Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- More
- Tutorials
- Practise Tests
- Interview Questions
- Free Courses
- Agile & PMP Practice Tests
- Agile Testing
- Agile Scrum Practice Exam
- CAPM Practice Test
- PRINCE2 Foundation Exam
- PMP Practice Exam
- Cloud Related Practice Test
- Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- AWS Solutions Architect
- AWS Developer Associate
- IT Related Pratice Test
- ITIL Practice Test
- Devops Practice Test
- TOGAF® Practice Test
- Other Practice Test
- Oracle Primavera P6 V8
- MS Project Practice Test
- Project Management & Agile
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Release Train Engineer Interview Questions
- Agile Coach Interview Questions
- Scrum Interview Questions
- IT Project Manager Interview Questions
- Cloud & Data
- Azure Databricks Interview Questions
- AWS architect Interview Questions
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Kubernetes Interview Questions
- Web Development
- CSS3 Free Course with Certificates
- Basics of Spring Core and MVC
- Javascript Free Course with Certificate
- React Free Course with Certificate
- Node JS Free Certification Course
- Data Science
- Python Machine Learning Course
- Python for Data Science Free Course
- NLP Free Course with Certificate
- Data Analysis Using SQL
- Home
- Blog
- Project Management
- Prince2 Risk Management Approach: Definition, Types
Prince2 Risk Management Approach: Definition, Types
Updated on Nov 22, 2022 | 15 min read | 9.4k views
Share:
Table of Contents
There is a specific PRINCE2 risk definition derived from the MoR® method i.e., Management of Risk method. It goes on to say that PRINCE2 risks are a compilation of occurrences that impact meeting the project objectives. It is an uncontrollable and uncertain event that can either negatively or positively affect the project objective.
Another way to define the impact is by seeing risk as an opportunity or a threat. Although most people might associate risk as a negative occurrence, a positive PRINCE2 risk management approach example or an opportunity might help you understand better. A project needs to be developed in a new CRM system with a risk that results in a 50% reduction on $15,000 worth of the warehouse integration module. This risk can be categorized as an opportunity that will more likely positively affect the project.
To ensure that risk management in the course of a project stays consistent and effective, you need to document how the risk management should be integrated into activities related to project management. Become a PRINCE2 practitioner and go for PRINCE2 Foundation and Practitioner certification to get the best learning experience.
PRINCE2 Risk Management Approach and Importance
The PRINCE2 risk management procedure recommends that every project have a risk management approach document unique to their prerequisites and objectives. This document will comprise all the project procedures related to risk management, elucidating how a risk needs to be identified, evaluated, handled, and communicated throughout the project.
Another foolproof risk management approach PRINCE2 describes the targeted risk management procedures and standards applicable during the project, including the responsibilities for facilitating consistency during the risk management. This might come off as a mammoth task, but if the project is part of a program, then a large chunk of this approach will be given to you already in a highly detailed template that can be updated as per the needs of the project.
You can make your job easier by using a PRINCE2 risk management template. The project manager creates the risk management approach (customized to suit the project) in the Initiation stage. The risk management strategy PRINCE2 consists of not only goals but also procedures and responsibilities/roles of risk management, including their reporting requisites. It can also consist of necessary details pertaining to the project, such as timing, tools, budget, and techniques associated with risk management procedures and interventions.
Master Right Skills & Boost Your Career
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session
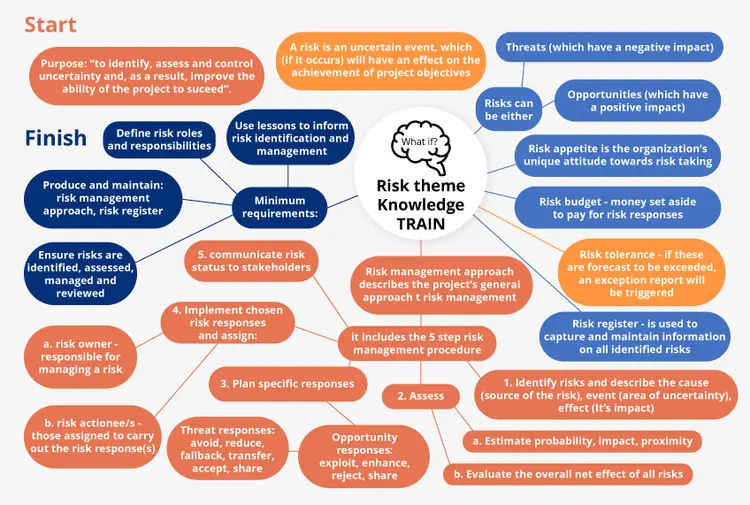
Another different yet surprisingly effective approach to risk management in PRINCE2 is risk-taking. Care should be taken during this approach because you need to consider the level of risk permitted by the project board. This level is also often termed risk tolerance. Suppose the risk exposure is expected to exceed said tolerance level allowed by the project board. In that case, the project manager needs to develop an exception report which he/she will need to submit to the project board to make a decision.
The project board needs to be flexible enough to take risk-related decisions that fall beyond the level of acceptance. Any risk that falls within the level of risk tolerance needs to be monitored lest there are any changes in the circumstances. In short, a foolproof exception report will enable the risk to be accepted.
PRINCE2 is a widely used methodology in risk management. It measures risk based on impact and likelihood for maximum efficiency in management. Since PRINCE2 defines risk as an opportunity, it helps fully comprehend the impact of a risk. This can extend beyond a project and portray how it can impact long-term business goals. Regardless of the risk's probability, nature, and implications, PRINCE2 empowers managers to manage it efficiently. The four main reasons why PRINCE2 is important in managing risks successfully have been elucidated below:
- PRINCE2 Helps Detect Risk as Soon as Possible: This is one of the reasons why PRINCE2 is one of the most widely used frameworks in risk management. During the initiation of PRINCE2 in a project, the most important part of it is its proactive identification of risks early on. It all begins with the creation of a Project Charter that is presented with great attention to detail consisting of the vision, scope, and project deliverables. This project planning level ensures that the teams can detect any related risks. Therefore, before launching a project, this framework emphasizes risk awareness as well as the intent to manage it from the very beginning.
- PRINCE2 Looks at Risk with a Broad Business Context: PRINCE2 helps weigh out the impact of the risk in question way beyond the stipulated schedule or the budget of the project. According to the PRINCE2 risk management principles, a project always ought to contain a 'business case' that justifies the importance and feasibility of a project. Threats pertaining to the project are bound to make an impact on the business's goals in the long term. Stakeholders who want to stay informed about the holistic implication of the risk will need to be briefed on ways the lost expenses will be recovered and who will be at the suffering end if the project deliverables are not delivered.
- PRINCE2 Helps Identify Risk in a Cohesive, Logical Fashion: The first stage in PRINCE2 risk management is to look for the cause of risk. Post this, managers will need to pinpoint the circumstances by which a risk is more likely to occur. These are termed ‘risk events.’ The former is defined as the ‘how’ of risk, and the latter is defined as the ‘where/when’ of the risk. Once you have a clear idea about what is what, you can easily predict the impact of the risk with higher accuracy.
- PRINCE2 Helps Identify Potential Impact of Risk: There are two PRINCE2 risk categories. These two metrics used to evaluate risks are:
- Probability
- Impact
Risks with a low impact on the project can be accepted under general circumstances, regardless of how likely they are to happen. However, high probability and high-impact risks need to be managed proactively or escalated to the project's board members for further evaluation.
5. PRINCE2 Provides Useful Guidelines for Responding to Risk: Some risks cannot be avoided, so you need to mitigate the ones avoidable by changing the project scope or schedule. Once the true level of the impact of the risk is evaluated, the main risk response categories PRINCE2 are identified:
PRINCE2 Risk Categories
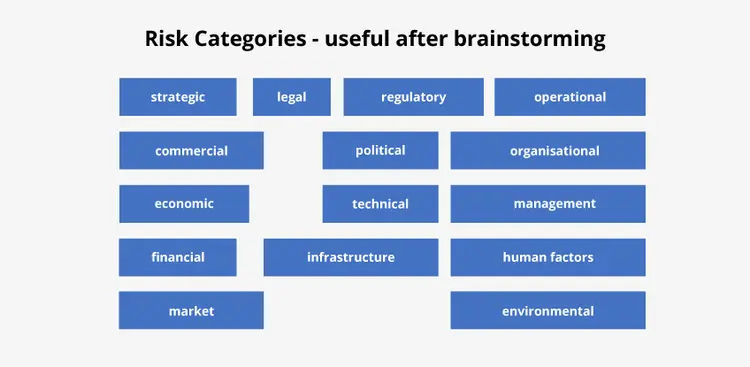
There are several PRINCE2 risk types. One of the best ways to categorize a PRINCE2 risk is by using the acronym PESTLE:
- Political
- Economic
- Sociological
- Technological
- Legal
- Environmental.
These categories can come in handy when breaking up the risks bit by bit so they can be evaluated in a more structured way, which further helps determine who should manage said risks and who should provide funds for the management.
Types of Risk Responses Identified by PRINCE2
There are nine types of PRINCE2 risk responses inside the framework of PRINCE2 risk management. These nine categories can further be categorized into three different groups:
- Response to opportunities
- Response to threats
- Response to both opportunities and threats
Risk Response Categories for Threats
- Avoid: In this instance, an alteration is made to mitigate or neutralize the threat that is more likely to make an impact on the project objectives. With these steps, an uncertain event can be actively avoided.
- Reduce: This is the action where steps are taken to reduce the impact or the probability of a risk. Similar to the ‘Avoid’ response, in this proactive response category, the action is taken prior to the risk occurrence.
- Prepare Contingency Plans: This response is carried out only if a risk takes place. Unlike ‘Avoid’ and ‘Reduce’, this response is more reactive than proactive one because it does not affect the probability of the risk. However, it actively mitigates the possible impact of the risk.
- Transfer: The financial impact of any risk can be transferred partly to a third party. To state an example, we can consider implementing penalty payments within the suppliers’ contracts because of late delivery or by availing insurance.
- Accept: This decision is a conscious one to do nothing. The acceptance of risk will require you to monitor it with the utmost care, ensuring that it does not move beyond the stipulated level of impact or probability.
Risk Response Categories for Opportunities
- Exploit: This action forces the risk event to occur.
- Enhance: As a direct opposite of the ‘Reduce’ response, this is a proactive response that increases the risk's impact or probability.
- Reject: This is a conscious decision not to do anything about the risk at hand. Similar to ‘Accept,’ a rejected risk or opportunity needs to be monitored thoroughly.
Risk Response Category for Both Threats and Opportunities
- Share: In certain instances, a procurement contract might consist of a pain/gain formula, as per which both the supplier and the customer share a gain, especially if estimated costs are lower than what was planned. They also share the pain if the costs exceed the expected rate. This response is actioned before the risk occurs.
Prince2 Risk Management Process
In a high-level PRINCE2 risk management plan, there are two stages:
- Risk Analysis
- Risk Management
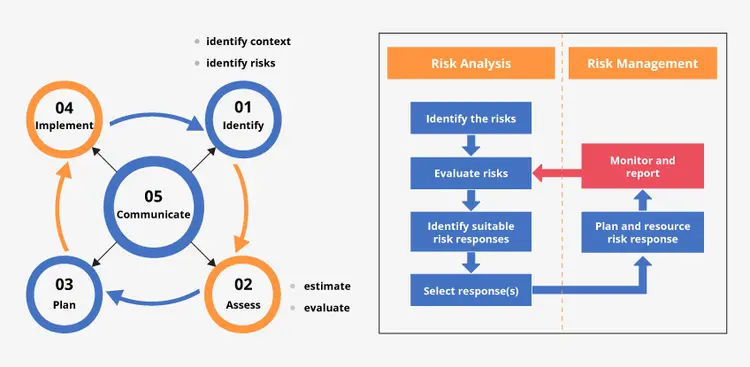
Risk Analysis
In the Risk Analysis stage, the following procedures take place:
- Risks are identified first.
- Risks are further assessed in terms of their impact, probability, risk proximity PRINCE2, and the like.
- The suitable responses for every risk in question are further pinpointed and considered.
- Finally, the most suitable response is chosen.
Risk Management
In the Risk Management stage, the following procedures take place:
- The chosen response is added to the relevant plan in the form of activity, in addition to the relevant resources required for carrying out the said activity.
- The second step is the approval of the stage plan, where the implementation and the effectiveness of the response activity are closely monitored. If the desired effect is not fulfilled, then a mode of corrective action needs to be carried out.
- The next step is reporting the risk status. This generally includes references within the Highlight Report and the Checkpoint Report.
If you are looking for a PRINCE2 risk management strategy example, there are many to consider. In PRINCE2, there are five steps in a risk management strategy that are recommended. The initial four steps are sequential. However, the communication step is actioned consistently and carried out in parallel with the previous four. The following five steps are unique to the PRINCE2 risk management framework: -
- Identify: The primary objective of the identify step is to attain information about a project so you can comprehend the stipulated objectives that fall under risk and to develop a risk management strategy suitable to the project to mitigate it without any added consequences. The risk management strategy denotes the process of risk management at the very inception of the project during its initiation stage. It is further thoroughly reviewed and even updated once a project stage ends. The Prince2 risk management strategy has to adhere to the corporate risk management policy or to the risk management strategy set by the program.
- Assess: PRINCE2 assessment of risk has two stages. They are:
- Estimation stage
- Evaluation stage
The main objective of the estimate stage is to evaluate the opportunities and threats related to the project based on their impact and probability – this can be done in various ways by using tools such as probability trees, expected value, Pareto analysis, and probability impact grid. The risk proximity also helps measure how quickly the risk will materialize if there is no action taken.
- Plan: Risk responses do always mitigate the risk at hand entirely. There is a possible chance of it leaving a residual risk. Integrating a risk response can sometimes remove or reduce any related risk. In this case, the risks might need to be seconded, i.e., the risks occurring can potentially invoke a risk response. Therefore, reviewing lessons from similar projects that have been taken up prior to the current one is of utmost importance during risk response planning. You need to take the effects of the possible responses into careful consideration as well.
- Implement: The Implement step ensures that the planned risk responses are actively actioned, their effectiveness monitored, and the right course of action is taken in instances where responses do not run in parallel with the expectations. An integral part of the implementation step is ensuring that clear responsibilities and roles are allocated to help the project manager in risk management.
- Communicate: Communication is a step that is continually actioned. This step should make sure that the relevant opportunity or risk-related information is properly conveyed internally to the project members and also externally to the stakeholders. Communication of these risks is an integral part of risk management.
PRINCE2 risk management is a valuable skill to have, especially in a business or a corporate setup. If you are a student or a professional looking to upgrade your skills in risk management, you can attain these with some of the best PRINCE2 Foundation training available online. These courses will enable you to have a holistic understanding of what risk management is and the processes involved in it.
People Involved in PRINCE2 Risks
A smooth workflow in the production process of an organization is very necessary because it will lead to the desired results that are in the project objectives. To ensure this happens, organizations worldwide hire the services of the following people who become involved in the risk management process:
- Corp/Programme: They aid in providing an extensive Corporate Risk Management policy as well as detailed information.
- Executive: They are responsible accountable for every aspect of Risk Management in a project. They help make sure of the existence of the Risk Management Approach in the organization and ensure that the follow-up process is actioned for the Business Case Risks.
- Senior User: They make sure that the risks related to the users are pinpointed, evaluated, and controlled.
- Senior Supplier: They ensure that the risks to the supplier are pinpointed, evaluated, and controlled.
- Project Manager: They help develop the Risk Management Approach document. They additionally create the Summary Risk Profile and Risk Register and help maintain them as well. They also make sure that the risks are consistently identified, evaluated, and controlled.
- Team Manager: They aid in identifying, evaluating, and controlling the risk.
- Project Assurance: They are responsible for reviewing the Risk Management practices against the project’s Risk Management Strategy.
- Project Support: They help Project Managers maintain the Risk Register of the projects.
It is quite easy to become a part of a risk management team if your interest lies in this field. All you need to do is take up Project Management course that will give you all the necessary skills and in-depth knowledge about this field of work.
What is PRINCE2 Risk Budget?
A Risk Budget is an amount of money that is kept separate to deal with certain stipulated responses to the threats and opportunities that come their way. It is a fixed amount of money that is not and cannot be utilized for any other purpose. Certain responses to the risk at hand will need certain actions to be carried out that cost money. The money that is budgeted in this stage is known as the Risk Budget.
What can the Risk Budget be Used for?
In the PRINCE2 risk management methodology, the risk budget is used for handling risks that are more likely to occur. They should strictly not be utilized in funding any extra requirements introduced later in the project. They should also not be used to cover the cost incurred due to the cause of project delays. Risk Budget is completely different from the Change Budget and has nothing to do with it. Therefore, it should not be considered an option if the Change Budget is exhausted.
Unlock your potential as a product owner with certified scrum product owner training! Develop agile leadership skills and deliver exceptional products. Join us today!
Conclusion
According to PRINCE2, ‘risk’ is an uncertain set of events, or an event can have either a positive or a negative impact on the project, should it occur. When it comes to the context of a project, it is the objectives of the project that are at risk. These project objectives include the completion of the project pertaining to numerous targets, typically considering factors like time, quality, cost, benefits, scope, and risk.
Therefore, risk management in any project can be tricky, and it will need skillful knowledge to carry it out successfully. To become a successful risk-managing executive, you need to have expert and keen skills in this field. You can develop them by taking up a very reliable online course that will give you the necessary push. KnowledgeHut PRINCE2 Foundation and Practitioner certification is a good place to start if you are looking for a good and flexible online course.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How many types of risk does PRINCE2 identify?
2. What are the 3 types of project risk?
3. What are some of the key activities in the risk management procedure PRINCE2?
4. Who is the risk owner in PRINCE2?
5. What are the three recommended types of issues in PRINCE2?
Get Free Consultation
By submitting, I accept the T&C and
Privacy Policy
