- Blog Categories
- Project Management
- Agile Management
- IT Service Management
- Cloud Computing
- Business Management
- Business Intelligence
- Quality Engineer
- Cyber Security
- Career
- Big Data
- Programming
- Most Popular Blogs
- PMP Exam Schedule for 2024: Check PMP Exam Date
- Top 60+ PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2024
- PMP Cheat Sheet and PMP Formulas To Use in 2024
- What is PMP Process? A Complete List of 49 Processes of PMP
- Top 15+ Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 170 Project Management Research Topics
- What is Effective Communication: Definition
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel in 2024?
- PMP Certification Exam Eligibility in 2024 [A Complete Checklist]
- PMP Certification Fees - All Aspects of PMP Certification Fee
- Most Popular Blogs
- CSM vs PSM: Which Certification to Choose in 2024?
- How Much Does Scrum Master Certification Cost in 2024?
- CSPO vs PSPO Certification: What to Choose in 2024?
- 8 Best Scrum Master Certifications to Pursue in 2024
- Safe Agilist Exam: A Complete Study Guide 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- SAFe vs Agile: Difference Between Scaled Agile and Agile
- Top 21 Scrum Best Practices for Efficient Agile Workflow
- 30 User Story Examples and Templates to Use in 2024
- State of Agile: Things You Need to Know
- Top 24 Career Benefits of a Certifed Scrum Master
- Most Popular Blogs
- ITIL Certification Cost in 2024 [Exam Fee & Other Expenses]
- Top 17 Required Skills for System Administrator in 2024
- How Effective Is Itil Certification for a Job Switch?
- IT Service Management (ITSM) Role and Responsibilities
- Top 25 Service Based Companies in India in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- What is Escalation Matrix & How Does It Work? [Types, Process]
- ITIL Service Operation: Phases, Functions, Best Practices
- 10 Best Facility Management Software in 2024
- What is Service Request Management in ITIL? Example, Steps, Tips
- An Introduction To ITIL® Exam
- Most Popular Blogs
- A Complete AWS Cheat Sheet: Important Topics Covered
- Top AWS Solution Architect Projects in 2024
- 15 Best Azure Certifications 2024: Which one to Choose?
- Top 22 Cloud Computing Project Ideas in 2024 [Source Code]
- How to Become an Azure Data Engineer? 2024 Roadmap
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 40 IoT Project Ideas and Topics in 2024 [Source Code]
- The Future of AWS: Top Trends & Predictions in 2024
- AWS Solutions Architect vs AWS Developer [Key Differences]
- Top 20 Azure Data Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- 25 Best Cloud Computing Tools in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Company Analysis Report: Examples, Templates, Components
- 400 Trending Business Management Research Topics
- Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK): Guide
- ECBA Certification: Is it Worth it?
- How to Become Business Analyst in 2024? Step-by-Step
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 20 Business Analytics Project in 2024 [With Source Code]
- ECBA Certification Cost Across Countries
- Top 9 Free Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates
- Business Analyst Job Description in 2024 [Key Responsibility]
- Business Analysis Framework: Elements, Process, Techniques
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Career Options after BCom to Know in 2024
- Top 10 Power Bi Books of 2024 [Beginners to Experienced]
- Power BI Skills in Demand: How to Stand Out in the Job Market
- Top 15 Power BI Project Ideas
- Top Picks by Authors
- 10 Limitations of Power BI: You Must Know in 2024
- Top 45 Career Options After BBA in 2024 [With Salary]
- Top Power BI Dashboard Templates of 2024
- What is Power BI Used For - Practical Applications Of Power BI
- SSRS Vs Power BI - What are the Key Differences?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Data Collection Plan For Six Sigma: How to Create One?
- Quality Engineer Resume for 2024 [Examples + Tips]
- 20 Best Quality Management Certifications That Pay Well in 2024
- Six Sigma in Operations Management [A Brief Introduction]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Six Sigma Green Belt vs PMP: What's the Difference
- Quality Management: Definition, Importance, Components
- Adding Green Belt Certifications to Your Resume
- Six Sigma Green Belt in Healthcare: Concepts, Benefits and Examples
- Most Popular Blogs
- Latest CISSP Exam Dumps of 2024 [Free CISSP Dumps]
- CISSP vs Security+ Certifications: Which is Best in 2024?
- Best CISSP Study Guides for 2024 + CISSP Study Plan
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker in 2024?
- Top Picks by Authors
- CISSP vs Master's Degree: Which One to Choose in 2024?
- CISSP Endorsement Process: Requirements & Example
- OSCP vs CISSP | Top Cybersecurity Certifications
- How to Pass the CISSP Exam on Your 1st Attempt in 2024?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Career Options & Courses After 12th Commerce in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- 30 Best Answers for Your 'Reason for Job Change' in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- Time Management Skills: How it Affects your Career
- Most Popular Blogs
- Top 28 Big Data Companies to Know in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Big Data Tools You Need to Know in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Web Development Using PHP And MySQL
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 30 Software Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- More
- Tutorials
- Practise Tests
- Interview Questions
- Free Courses
- Agile & PMP Practice Tests
- Agile Testing
- Agile Scrum Practice Exam
- CAPM Practice Test
- PRINCE2 Foundation Exam
- PMP Practice Exam
- Cloud Related Practice Test
- Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- AWS Solutions Architect
- AWS Developer Associate
- IT Related Pratice Test
- ITIL Practice Test
- Devops Practice Test
- TOGAF® Practice Test
- Other Practice Test
- Oracle Primavera P6 V8
- MS Project Practice Test
- Project Management & Agile
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Release Train Engineer Interview Questions
- Agile Coach Interview Questions
- Scrum Interview Questions
- IT Project Manager Interview Questions
- Cloud & Data
- Azure Databricks Interview Questions
- AWS architect Interview Questions
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Kubernetes Interview Questions
- Web Development
- CSS3 Free Course with Certificates
- Basics of Spring Core and MVC
- Javascript Free Course with Certificate
- React Free Course with Certificate
- Node JS Free Certification Course
- Data Science
- Python Machine Learning Course
- Python for Data Science Free Course
- NLP Free Course with Certificate
- Data Analysis Using SQL
- Home
- Blog
- Project Management
- Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2®
Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2®
Updated on Mar 06, 2021 | 10 min read | 8.3k views
Share:
Apart from Project Management Professional (PMP)®, PRINCE2® (PRojects IN Controlled Environments) is one of the most widely used methods for managing projects across the globe. It is a very methodical way of managing projects based on experience drawn from various projects and from the contributions of numerous people who worked using PRINCE2, such as project sponsors, project managers, project teams, academics, trainers and consultants.
Its generic design can be applied to any project regardless of project scale, type, organization, geography or culture.
- It separates the project management work from specialist contributions, like design or construction
- Focus is on describing what needs to be done, instead of prescribing how project is to be done.
PRINCE2®:
- is based more on governance for project management
- is tailored to meet the needs of the organization
- is implemented alongside industry-specific models e.g. ’engineering models’ or ‘development lifecycles’
- helps participants focus on the viability of the project in relation to objectives mentioned in the business case
- makes sure that everybody involved is represented in planning and decision-making, appropriately
- inspires to learn lessons from experience in the projects and helps in continual improvement within the organizations.
PRINCE2 in Project Management
Some characteristics of project work that differentiates itself from business as usual (BAU) are:-
- Change - Projects are a great catalyst for introducing change.
- Temporary - Projects have a definite start and a definite end.
- Cross-functional - people having different skills work together
- Unique - each project will be unique such as it involves a different customer, a different time. a different team, a different location
- Uncertainty – All projects carry a very high uncertainty – threats and opportunities.
What are six project constraints that we wish to control throughout a project
Master Right Skills & Boost Your Career
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session
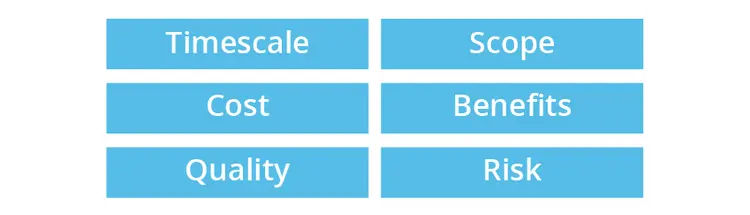
- Costs – spending depends on the budget given to the project manager
- Timescales - A question the project manager is most frequently asked: What is your expected project completion date?
- Quality - products must be fit for the purpose for which they are produced.
- Scope – What is in-scope and out-of-scope of the project
- Benefits – What is the reason for doing this? A very crystal-clear understanding of the purpose of the project is required by the project manager
- Risk - All projects are risky but project manager must be aware of exactly how much risk we are in a position to accept
PRINCE2 assumes that there will be -
- a customer who will specify the requirement of a product
- a supplier who will provide all skilled resources to deliver that product
PRINCE2 Structure
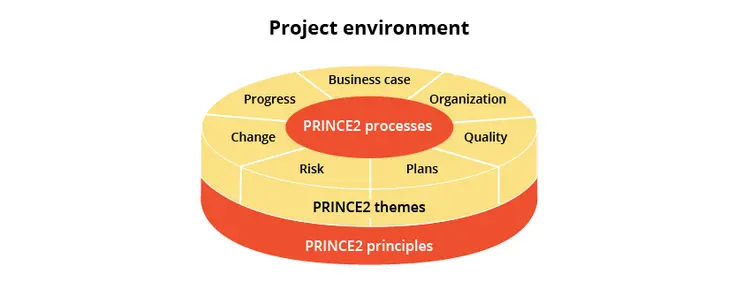
The PRINCE2 Seven Principles are:-
1. Continued business justification - A PRINCE2 project has continued business justification.
All PRINCE2 projects require that:
- for starting the project, there has to be a justifiable reason
- this justification must be recorded and approved
- the justification must remain valid and is revalidated, throughout the project life-cycle to ensure that the project remains in line with the benefits which contribute to business objectives
- justification is documented either as a business case document or may use some business plans or any other similar document
2. Learn from experience - lessons learned (seek), recorded and acted upon throughout the project.
3. Defined roles and responsibilities - within an organization structure engages the business, user and supplier stakeholder interests
4. Manage by stages - A PRINCE2 project is planned, monitored and controlled on a stage-by-stage basis.
In PRINCE2, a project must have at least two management stages:
- an initiation stage
- at least one further management stage.
5. Manage by exception - tolerances are defined for each project objective, to set limits for delegating authority.
6. Focus on products – focus is more on the defining the products and delivery of products, including quality requirements.
7. Tailor to suit the environment - PRINCE2 can be tailored to suit the project size, complexity, team capability, environment, importance and risk. Project manager and project board will have to make choices including decisions on how PRINCE2 should be applied on the project.
PRINCE2 Seven Themes
The PRINCE2 Seven Themes are -
- Business Case (Why?): a project usually starts with an idea or a concept which is then considered to have potential value for the organization concerned. This theme addresses how the idea is developed into a viable investment proposition for the organization and how project management maintains the focus on the organization’s objectives throughout the project.
- Organization (Who?): organization which commissions the project needs to allocate the work to managers who will be responsible for it and steer it through to completion. Projects are cross-functional. This theme describes the roles and responsibilities the project management team is required to have, in order to manage the project efficiently and effectively.
- Quality (What?): all participants understand the quality attributes of the products to be delivered and then how the project management will ensure that these requirements are ultimately delivered.
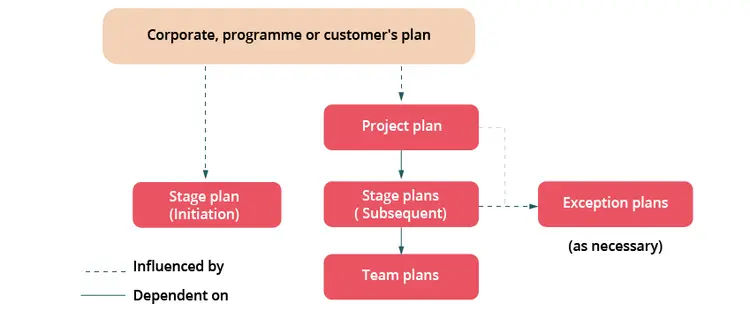
- Plans (How? How much? When?):
- project plan for the project as a whole, will usually be a high-level plan, providing indicative timescales, milestones, cost and resource requirements based on estimates
- detailed stage plan for the current management stage, aligned with the overall project plan timescales, produced before the start of that stage
- exception plans show actions performed to recover or come back on track from or avoid a forecast deviation from agreed tolerances, applies to project plan or stage plan
- a number of work packages are developed using detailed team plan
- Risk (What if?): addresses how project management manages uncertainty.
- Change (What is the impact?): describes how project management assesses and responds to issues which have a potential impact on any of the baseline aspects of the project such as its plans and completed products. Issues may be instances of a product not meeting its specification or requests for change or unanticipated general problems.
- Progress (Where are we now? Where are we going? Should we carry on?): addresses the ongoing viability of the plans. This theme monitors actual performance, explains the decision-making process for approving plans and the escalation process if events do not go according to plan. Ultimately, it determines how and whether the project should proceed.
PRINCE2 Seven Processes
The PRINCE2 Seven Processes are:-
Starting Up A Project (SU)
Purpose
- to ensure that the prerequisites for initiating a project are in place by answering the question: Do we have a viable and worthwhile project?
- base information needed to make rational decisions such as commissioning of the project is defined, key roles and responsibilities are identified and resources are allocated and a foundation for detailed planning is made available.
Objective: To ensure that:
- a business justification is documented in an outline business case, for initiating the project
- necessary authorities exist, for initiating the project
- project brief is available to define and confirm the scope of the project
- a feasible project approach is selected after evaluating different delivery approaches
- individuals are appointed who will undertake the project work
- the work required for project initiation is planned and documented in a stage plan
Directing A Project (DP)
Purpose: To enable project board
- to be accountable for the project’s success by making key decisions and exercising overall control of the project and
- delegating day-to-day management of the project to the project manager
Objective
To ensure that
- some authority exists to initiate the project, to deliver the products and close the project
- management direction and control are provided to all concerned throughout the project’s life
- project remains viable at every stage
- corporate, programme management or the customer has a transparent interface to the project
- post-project benefits realization plans are reviewed and managed
Initiating A Project (IP)
Purpose
- to establish a sturdy foundation for the project
- to understand the work that needs to be done to deliver the project’s products before committing to a large spend
Objective: to ensure that there is a common understanding of -
- what are the reasons for doing the project, what benefits are expected and what are the associated risks
- what is the scope of the work and what are the products to be delivered
- how the products will be delivered, when should they be delivered and what would be the cost involved at that point of time
- What the project decision-making team is comprised of
- how the required level of quality is be achieved
- how baselines can be established and controlled
- how risks, issues and changes can be identified, assessed and controlled
- how progress of the project can be monitored and controlled
- who requires which information, in what format and at what point of time
Controlling A Stage (CS)
Controlling A Stage (CS)
Purpose: To assign and monitor work, deal with issues, report progress to the project board and take corrective actions to ensure that the management stage remains within tolerance
Objective: to ensure that:
- proper attention is focused on delivery of the management stage’s products by monitoring to avoid uncontrolled change and loss of focus
- risks and issues are tracked to keep them under control
- business case is reviewed at appropriate times
- agreed products for the management stage are delivered to stated quality standards, within cost, effort and time agreed
- project management team is focused on delivering within the tolerance level set
Managing Product Delivery (MPD)
Purpose: is to control the link between the project manager and the team manager(s). Both agree on requirements for acceptance, execution and delivery.
Objective: to ensure that:
- product related work allocated to the team is authorized and agreed upon first
- team managers, team members and suppliers are clear about what needs to be produced and what is the expected effort, cost or timescales
- planned products are delivered to expectations and within tolerances
- accurate information on progress of product development should be provided to the project manager at an agreed frequency to ensure that expectations are managed
Managing a Stage Boundary (SB)
Purpose: to enable the project manager to provide the project board with sufficient information to be able to:
- review the current management stage if it has completed successfully
- approve the next stage plan
- review the updated project plan
- confirm continued business justification and acceptability of the risks
Hence, this process should either be executed at the end of or close to the end of each management stage.
Objective: is to:
- give an assurance to the project board that all products produced in the stage plan for the current management stage are developed by the team and approved
- prepare the next management stage plan
- review the PID documents and if necessary, update the business case, project plan, project approaches, project management team structure and role descriptions
- provide all the accurate information required by the project board to assess the continuing viability of the project
- record any information gathered or lessons learned that can help later management stages of the current project and/or other/future projects
- request authorization to start the next management stage from the project board
For exceptions, the objectives are to:
- review the PID documents and if necessary, update the customer’s quality expectations, project approaches and controls and role descriptions
- provide all the accurate information required by the project board to assess the continuing viability of the project
- prepare an exception plan as directed by the project board
- without fail and further delay project manager must seek approval to replace the project plan or stage plan for the current management stage with the exception plan
Managing a stage boundary is not performed towards the end of the final management stage, except an exception plan may be created on need basis.
Closing A Project (CP)
Purpose
- provide a normal termination point at which acceptance of the project’s product is confirmed and accepted by the user group
- recognize that objectives set out in the original PID documents have been achieved (or approved changes to the objectives have been achieved), or that the project has nothing more to contribute
Objective
- verify that the final product has been accepted by the user
- make sure that the operations are able to support the products when the project is disbanded
- review the performance of the project against its baselines
- assess any benefits that have been realized during the project cycle and update the benefits management approach to include any post-project benefit reviews
- ensure that provision has been made to address all open issues and risks, with follow-on action recommendations
Team roles in PRINCE2
Project Board
Members: Executive, Senior Users and Senior Suppliers
Responsibilities
- Accountable for the success or failure of the project
- Provides unified direction to the project
- Delegates effectively
- Facilitates integration
- Authorizes the funds
- Effective decision-making
- Supports the project manager
- Ensures effective communication
Executive
- Appointed by Corporate, Programme management or Customer
- Ultimately responsible for the project
- Key decision maker, buck stops at him
- Ensures project is focused throughout its life on achieving its objectives
- Ensures project delivers value for money
- Ensures project is aligned to corporate strategy.
Responsibilities
- Design and appoint project management team
- Oversee development of the Project Brief
- Oversee development of detailed Business Case
- Secure funding for the project
- Hold Senior Supplier accountable for the quality and integrity of the product
- Hold Senior User accountable for realizing the benefits
- Monitor and control the progress at strategic level
- Chair Project Board reviews
Project Manager
- Given authority to run the project on a day to day basis
- Ensures that the project produces the required products
- Responsible for producing the result capable of achieving the benefits as stated in the business case
Responsibilities
- Produce key project documents
- Prepare key project reports
- Maintain key project records
- Liaise with corporate, programme management or customer
- Liaise with external suppliers
- Lead and motivate the project management team
- Manage information flows between various levels of the project
- Manage production of the required products
- Establish and manage the project procedures
- Authorize Work Packages
- Advise the Project Board of any deviations from the plan
Senior User
- Specifies the needs of those who will use the project’s products.
- Represents the interests of :
- Those who will use the project’s products.
- Those for whom the products will achieve an objective
- Those who will use the products to deliver benefits
Responsibilities
- Provide the customer’s quality expectations
- Ensure project products deliver the desired outcomes
- Ensure that expected benefits are realized
- Resolve user requirements and priority conflicts
- Ensure availability of user resources
- Make decisions on escalated issues
- Undertake Project Assurance from user perspective
Senior Supplier
- Represents interest of those producing the project products
- Accountable for quality of products delivered by the supplier
- Responsible for technical integrity of the project
Responsibilities
- Assess the viability of the project
- Ensure that proposals are realistic
- Advise on the selection of product methods
- Ensure that supplier resources are made available
- Make decisions on escalated issues
- Resolve supplier requirements and priority conflicts
- Ensure adherence to quality procedures
- Undertake Project Assurance from supplier perspective.
Project Assurance
- Covers the primary stakeholder interests
- Has to be independent of the Project Manager
- Has sufficient credibility
- May be from corporate, programme management or customer organization.
Responsibilities
- Liaison between business, user and supplier is maintained
- Risks are controlled
- Right people are involved in writing product descriptions
- Right people are planned and involved in quality inspections
- Staff are properly trained in quality methods
- Quality methods are adhered to
- An acceptable solution is being developed
- Applicable standards are being used
Change Authority
- Authority for approving responses to requests for change or off-specifications
- Adequately represents the business, user and supplier interests
- Has sufficiently credibility
- Change Authority could be assigned to:
- Corporate or Programme management
- Project Board
- A nominated person / body
- Project Manager.
Responsibilities
- Review and approve or reject all requests for change and off-specifications within the delegated limits of authority and change budget set by the Project Board.
- Refer to the Project Board if any delegated limits of authority or allocated change budget are forecast to be exceeded.
Project Support
- Is mainly concerned with providing administrative services or advice and guidance on the use of project management tools.
- Is the responsibility of the Project Manager.
- May be delegated to other roles or a separate role.
- Project Support and Project Assurance roles must be kept separate.
Responsibilities
- Set up and maintain project files
- Establish document control procedure
- Collect data – actuals and forecasts
- Update plans and maintain them
- Administer quality review progress
- Administer project board meetings
- Assist with compilation of reports
- Contribute expertise in tools and techniques
- Maintain key records
- Administer the configuration management procedure.
Team Manager
- Reports to and takes direction from the Project Manager
- Responsible to ensure production of products allocated by the Project Manager
- Reasons for allocating a separate Team Manager :
- Size of the project
- Specialist skills or knowledge needed
- Geographical location, or
- Preferences of the Project Board.
Responsibilities
- Prepare the Team Plan
- Produce Checkpoint Reports
- Plan, monitor and manage the team’s work
- Ensure progress of team’s work and use of team resources
- Identify any issues and risks associated with a Work Package
- Advise Project Manager of any deviations
- Hand over completed and approved products
- Liaise with Project Assurance and Project Support roles
- Plan and manage quality activities relating to team’s work.
Looking for the best PRINCE2 foundation training online? Look no further than our expert-led program! With our comprehensive course, you'll gain the skills and knowledge needed to become a certified PRINCE2 and take your project management career to the next level. Enroll now and elevate your career with ease!
Types of PRINCE2 documentation
Throughout PRINCE2 project, documentation is maintained as management products.
There are three types of management product: baselines, records and reports.
Baseline management products: are those that define aspects of the project and, when approved, are subject to change control. These are:
- Benefits management approach
- Business case
- Change control approach
- Communication management approach
- Plan (covers project plans, stage plans, exception plans and, optionally, team plans)
- Product description
- Project brief
- Project initiation documentation (PID)
- Project product description
- Quality management approach
- Risk management approach
- Work package
Records management products: are dynamic and they maintain information regarding project progress. These are:
- Configuration item record
- Daily log
- Issue register
- Lessons log
- Quality register
- Risk register.
Reports management products: provide a snapshot of the status of certain aspects of the project. These are:
- Checkpoint report
- End project report
- End stage report
- Exception report
- Highlight report
- Issue report
- Lessons report
- Product status account
Summary
PRINCE2 is PRojects IN Controlled Environments
- separates the management of project work from the specialist contributions, such as design or construction.
- focuses on describing what needs to be done, rather than prescribing how everything is to be done focusing on describing what needs to be done, rather than prescribing how everything is done.
Characteristics of project work that differentiates itself from business as usual (BAU) are Change, Temporary, Cross-functional, Unique and Uncertainty
We wish to control Cost, Timescale, Scope, Quality, Benefits and Risk on a PRINCE2 project
PRINCE2 assumes that there will be -
- a customer who will specify the desired result
- a supplier who will provide the resources and skills to deliver that result
PRINCE2 principles are :-
- Continued business justification
- Learn from experience
- Defined roles and responsibilities
- Manage by stages
- Manage by exception
- Focus on products
- Tailor to suit the project
PRINCE2 Themes are :-
- Business Case
- Organization
- Quality
- Plans
- Risk
- Change
- Progress
PRINCE2 processes are :-
- Starting Up a Project (SU)
- Directing A Project (DP)
- Initiating A Project (IP)
- Controlling A Stage (CS)
- Managing Product Delivery (MPD)
- Managing a Stage Boundary (SB)
- Closing A Project (CP)
PRINCE2 Team roles are – Project Board (Executive, Senior User and Senior Supplier), Project Manager, Team Manager, Project Assurance, Change Authority and Project Support
Throughout PRINCE2 project, documentation is maintained as management products - baselines, records and reports.
Get Free Consultation
By submitting, I accept the T&C and
Privacy Policy
