- Blog Categories
- Project Management
- Agile Management
- IT Service Management
- Cloud Computing
- Business Management
- Business Intelligence
- Quality Engineer
- Cyber Security
- Career
- Big Data
- Programming
- Most Popular Blogs
- PMP Exam Schedule for 2024: Check PMP Exam Date
- Top 60+ PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2024
- PMP Cheat Sheet and PMP Formulas To Use in 2024
- What is PMP Process? A Complete List of 49 Processes of PMP
- Top 15+ Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 170 Project Management Research Topics
- What is Effective Communication: Definition
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel in 2024?
- PMP Certification Exam Eligibility in 2024 [A Complete Checklist]
- PMP Certification Fees - All Aspects of PMP Certification Fee
- Most Popular Blogs
- CSM vs PSM: Which Certification to Choose in 2024?
- How Much Does Scrum Master Certification Cost in 2024?
- CSPO vs PSPO Certification: What to Choose in 2024?
- 8 Best Scrum Master Certifications to Pursue in 2024
- Safe Agilist Exam: A Complete Study Guide 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- SAFe vs Agile: Difference Between Scaled Agile and Agile
- Top 21 Scrum Best Practices for Efficient Agile Workflow
- 30 User Story Examples and Templates to Use in 2024
- State of Agile: Things You Need to Know
- Top 24 Career Benefits of a Certifed Scrum Master
- Most Popular Blogs
- ITIL Certification Cost in 2024 [Exam Fee & Other Expenses]
- Top 17 Required Skills for System Administrator in 2024
- How Effective Is Itil Certification for a Job Switch?
- IT Service Management (ITSM) Role and Responsibilities
- Top 25 Service Based Companies in India in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- What is Escalation Matrix & How Does It Work? [Types, Process]
- ITIL Service Operation: Phases, Functions, Best Practices
- 10 Best Facility Management Software in 2024
- What is Service Request Management in ITIL? Example, Steps, Tips
- An Introduction To ITIL® Exam
- Most Popular Blogs
- A Complete AWS Cheat Sheet: Important Topics Covered
- Top AWS Solution Architect Projects in 2024
- 15 Best Azure Certifications 2024: Which one to Choose?
- Top 22 Cloud Computing Project Ideas in 2024 [Source Code]
- How to Become an Azure Data Engineer? 2024 Roadmap
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 40 IoT Project Ideas and Topics in 2024 [Source Code]
- The Future of AWS: Top Trends & Predictions in 2024
- AWS Solutions Architect vs AWS Developer [Key Differences]
- Top 20 Azure Data Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- 25 Best Cloud Computing Tools in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Company Analysis Report: Examples, Templates, Components
- 400 Trending Business Management Research Topics
- Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK): Guide
- ECBA Certification: Is it Worth it?
- How to Become Business Analyst in 2024? Step-by-Step
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 20 Business Analytics Project in 2024 [With Source Code]
- ECBA Certification Cost Across Countries
- Top 9 Free Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates
- Business Analyst Job Description in 2024 [Key Responsibility]
- Business Analysis Framework: Elements, Process, Techniques
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Career Options after BCom to Know in 2024
- Top 10 Power Bi Books of 2024 [Beginners to Experienced]
- Power BI Skills in Demand: How to Stand Out in the Job Market
- Top 15 Power BI Project Ideas
- Top Picks by Authors
- 10 Limitations of Power BI: You Must Know in 2024
- Top 45 Career Options After BBA in 2024 [With Salary]
- Top Power BI Dashboard Templates of 2024
- What is Power BI Used For - Practical Applications Of Power BI
- SSRS Vs Power BI - What are the Key Differences?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Data Collection Plan For Six Sigma: How to Create One?
- Quality Engineer Resume for 2024 [Examples + Tips]
- 20 Best Quality Management Certifications That Pay Well in 2024
- Six Sigma in Operations Management [A Brief Introduction]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Six Sigma Green Belt vs PMP: What's the Difference
- Quality Management: Definition, Importance, Components
- Adding Green Belt Certifications to Your Resume
- Six Sigma Green Belt in Healthcare: Concepts, Benefits and Examples
- Most Popular Blogs
- Latest CISSP Exam Dumps of 2024 [Free CISSP Dumps]
- CISSP vs Security+ Certifications: Which is Best in 2024?
- Best CISSP Study Guides for 2024 + CISSP Study Plan
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker in 2024?
- Top Picks by Authors
- CISSP vs Master's Degree: Which One to Choose in 2024?
- CISSP Endorsement Process: Requirements & Example
- OSCP vs CISSP | Top Cybersecurity Certifications
- How to Pass the CISSP Exam on Your 1st Attempt in 2024?
- Most Popular Blogs
- Best Career options after BA [2024]
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Career Options & Courses After 12th Commerce in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- 30 Best Answers for Your 'Reason for Job Change' in 2024
- Recommended Blogs
- Time Management Skills: How it Affects your Career
- Most Popular Blogs
- Top 28 Big Data Companies to Know in 2024
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top Big Data Tools You Need to Know in 2024
- Most Popular Blogs
- Web Development Using PHP And MySQL
- Top Picks by Authors
- Top 30 Software Engineering Projects in 2024 [Source Code]
- More
- Tutorials
- Practise Tests
- Interview Questions
- Free Courses
- Agile & PMP Practice Tests
- Agile Testing
- Agile Scrum Practice Exam
- CAPM Practice Test
- PRINCE2 Foundation Exam
- PMP Practice Exam
- Cloud Related Practice Test
- Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- AWS Solutions Architect
- AWS Developer Associate
- IT Related Pratice Test
- ITIL Practice Test
- Devops Practice Test
- TOGAF® Practice Test
- Other Practice Test
- Oracle Primavera P6 V8
- MS Project Practice Test
- Project Management & Agile
- Project Management Interview Questions
- Release Train Engineer Interview Questions
- Agile Coach Interview Questions
- Scrum Interview Questions
- IT Project Manager Interview Questions
- Cloud & Data
- Azure Databricks Interview Questions
- AWS architect Interview Questions
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Kubernetes Interview Questions
- Web Development
- CSS3 Free Course with Certificates
- Basics of Spring Core and MVC
- Javascript Free Course with Certificate
- React Free Course with Certificate
- Node JS Free Certification Course
- Data Science
- Python Machine Learning Course
- Python for Data Science Free Course
- NLP Free Course with Certificate
- Data Analysis Using SQL
T-Shirt Sizing: An Agile Estimation Guide 2025
By Lindy Quick
Updated on Feb 04, 2025 | 8 min read | 21.2k views
Share:
In the Agile Management training , the concept of T-shirt sizing stands out as a novel and increasingly adopted estimation method. This Agile t-shirt sizing, mirroring the simplicity of T-shirt size labels like Small, Medium, Large, and Extra Large, applies these categories to gauge the scale of project tasks. It's especially appreciated for its collaborative nature and straightforward approach, making it easier for teams to evaluate and discuss project workload and complexity.
What Exactly is T-Shirt Sizing in Agile?
Agile T-shirt sizing is one of the simplest project estimation techniques used by software development teams. T-shirt sizing techniques offer several benefits in project management, especially in the early stages of a project.

Insider Tips to Land Your Dream Scrum Master Job
Includes Scrum Resume Sample
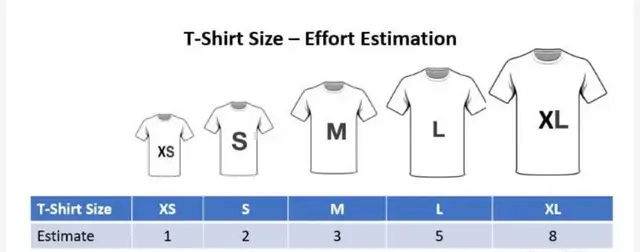
Here are additional points that highlight its usefulness:
- Improved Collaboration: Agile t-shirt sizing promotes a collaborative environment by encouraging team members to discuss and agree on sizing estimates. This collaborative approach helps build a mutual understanding of the project among team members.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: This method is highly adaptable to change. As your project evolves and more information becomes available, you can easily modify and update the t-shirt size, making it a dynamic project management tool.
- Facilitates Faster Decision-Making: T-Shirt Sizing allows for faster quotes and a faster decision-making process. This speed is advantageous in the initial stages of a project when time is often a critical factor and quick decisions need to be made to move the project forward.
You might also find it interesting to read about 5 whys root cause analysis article.
How Does T-Shirt Sizing Work?
Here's how T-shirt sizing functions in the Agile:
- Defining T-Shirt Sizes: Initially, teams establish a range of sizes, often including Small, Medium, Large, and Extra Large. These sizes might expand to Extra Small or XXL for more detailed differentiation, symbolizing varying levels of task complexity and effort.
- Understanding Size Implications: Each size acts as a qualitative marker. For example, a 'Small' task might imply something quick and simple, while a 'Large' task indicates greater complexity and time investment. A shared team understanding of each size's meaning is crucial for consistent estimation.
- Involving the Team in Sizing: The sizing process is typically a team effort, involving developers, testers, and sometimes product owners. This collective approach benefits from diverse viewpoints and fosters a sense of shared responsibility in understanding project scope.
- Assigning Sizes to Tasks: In planning or estimation meetings, the team discusses each task, assigning a T-shirt size. This step encourages open dialogue and relies on team members' experiences and knowledge.
- Evaluating Workload: Post-sizing, teams can better assess the overall workload, plan sprints, allocate resources, and set realistic timelines, understanding that larger sizes indicate tasks of greater complexity or duration.
What is T-Shirt Sizing Estimation Technique?
The T-shirt sizing technique is particularly useful in early project phases when detailed information is scarce. It's a more intuitive and relative approach compared to traditional methods focused on hours or days, thus enhancing team communication and project understanding.
- Collaborative Estimation: During the estimating session, team members discuss and collectively assign a T-shirt size to each task. This process fosters team participation and leverages the collective knowledge and experience of team members.
- Intuitive and non-technical: This method uses simple, familiar terminology, such as T-shirt size, so it is easy to understand and does not require technical expertise. This is especially useful for teams with diverse backgrounds or for stakeholders not deeply involved in the project's technical aspects.
- Focus on early stages: T-shirt sizing is most useful during the early stages of a project, when detailed information about tasks and features is not yet available. It provides a comprehensive and quick way to assess the scope and complexity of a project.
- Improved communication and understanding: T-shirt sizes facilitate communication within your team and with stakeholders. This simplifies discussions about project scope and requirements and improves overall understanding of the project.
- Flexibility: This method allows for flexibility and adaptability. As the project progresses and more information becomes available, you can adjust the initial T-shirt size or convert it into a more accurate estimate, such as hours or days.
- Prioritization and Planning: T-shirt sizing helps prioritize tasks and plan sprints in agile project management. You can separate tasks into smaller tasks to make them easier to manage.
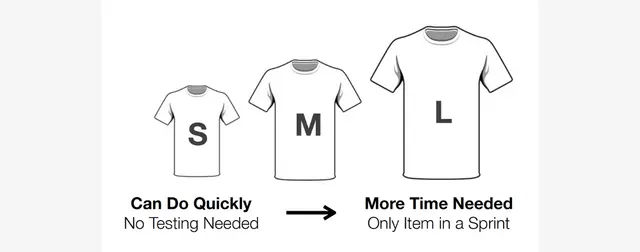
Steps Involved in T-Shirt Size Estimate
In practical terms, the T-shirt sizing process in Agile involves:
- Gathering Requirements: Understanding project needs fully before sizing begins.
- Initial Sizing of Tasks: Assigning initial T-shirt sizes based on complexity and effort needed.
- Team Collaboration and Discussion: Detailed task discussions to achieve a sizing consensus.
- Comparing with Past Projects: Using historical data for better accuracy in sizing.
- Reaching Consensus: Aiming for team agreement on sizes.
- Flexibility for Adjustments: Revisiting sizes as the project evolves and more information becomes available.
Pros and Cons of T-Shirt Sizing in Agile
Advantages of T-shirt sizing in Agile
- Simplicity and Accessibility: Agile's T-shirt size chart is simple, easy to understand, and easy for team members to use. This simplicity helps with quick adjustment and uptake, especially for teams new to agile methodologies.
- Easier relative estimating: agile t shirt sizing estimation encourages team members to think in relative size and complexity rather than trying to set exact hours or days. This aligns well with the agile philosophy of flexible scheduling.
- Improved team collaboration: When sizing T-shirts in Agile, team members discuss and agree on the size, fostering collaboration and collective understanding of the scope and complexity of the project.
- Reduce Analysis Paralysis: The Agile T-Shirt Sizing Diagram provides a high-level view that prevents teams from getting lost in the details during the early stages of planning, thereby reducing analysis paralysis.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Agile's T-shirt size chart is customizable. These can easily adapt to different team dynamics and project complexities, providing a flexible estimation approach.
Disadvantages of T-shirt sizing in Agile:
- Lack of precision: T-shirt size estimation is inherently inaccurate. This can create resource allocation and budgeting challenges that require more accurate estimates.
- Potential for Misinterpretation: Due to the subjective nature of T-shirt sizing, team members may interpret each size differently, resulting in discrepancies.
- Not suitable for all projects: Agile T-shirt sizing is most effective for projects that require detailed planning and accurate estimates, such as projects with fixed budgets and tight schedules.
- Scalability issues: As the project becomes more complex, estimating the T-shirt size effort may become less effective. Larger projects may require more advanced and detailed estimation techniques.
- Dependence on Team Experience: The effectiveness of T-shirt sizing in Agile is highly dependent on the team's experience and understanding of the project. New or inexperienced teams may find it difficult to assign sizes accurately.
Achieve your career goals with our PMP course objectives. Enroll now to enhance your skills in project management and prepare for the PMP certification exam.
Planning Poker – A Better Alternative to T-Shirt Sizing
Planning Poker combines expert opinion, analogy, and disaggregation to deliver effective estimates.
By playing this "game," teams come together to discuss and evaluate their work, making it an exciting and collaborative process.
The values on the cards typically follow a modified Fibonacci sequence (0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, etc.) and reflect the inherent uncertainty in estimating larger items.
How Planning Poker Works Presenting User Stories:
The Product Owner or Moderator presents user stories or tasks to the team.
- Initial discussion: Team members discuss story requirements and raise questions and concerns.
- Individual Rating: Each team member selects a card that represents their rating of the effort or complexity involved.
- Publish and compare quotes: All team members simultaneously publish cards and view their personal quotes.
- Discuss discrepancies: If there are significant discrepancies in the estimates, the team discusses the reasons for the differing views.
- Retry Estimate: The process repeats until the team reaches a consensus.
Advantages of Planning Poker over T-Shirt Sizing
- More Nuanced Estimates: Planning Poker allows for a broader range of estimates than the broad category of T-Shirt Sizing, resulting in more nuanced and detailed planning becoming possible.
- Facilitate team discussion: This process inherently involves team discussion and consensus building, which promotes better understanding and coordination.
- Avoiding Anchoring Bias: Because quotes are created one at a time and announced simultaneously, Planning Poker reduces the risk of team members being influenced by the first quote they hear.
- Suitable for complex projects: This method is suitable for projects where the tasks vary in complexity and require more accurate estimates.
- Engaging and Fun: Planning Poker adds gamification elements to the estimation process, making it more appealing to team members.
Disadvantages of Planning Poker
- Time-consuming: This method can be more time-consuming than sizing a T-shirt, especially for teams new to the process or for projects with many user stories.
- Requires an experienced team: The effective use of Planning Poker depends on the team's experience and understanding of work and agile processes.
- Possible Cognitive Bias: Despite efforts to minimize bias, factors such as groupthink and the influence of senior team members can still influence estimates.
- Problems with remote settings: Although digital tools exist, effectively coordinating planning poker with remote or distributed teams can be more difficult.
- Comparison to T-Shirt Sizing T-Shirt Sizing is easy and quick but lacks the accuracy and detailed discussion that Planning Poker provides.
Planning Poker uses an iterative, consensus-oriented approach that results in more accurate and reliable estimates, especially for complex tasks. However, it requires more time and active team participation.
Delivery planning with T-shirt estimates
The t-shirt sizing is a great way of providing initial estimates and can be used as a first round of estimating, providing stakeholders and the team with a relative or broad idea of the time and effort required for the project.
As mentioned above, it is often the first round of planning and starts with the project being split into high-level epics which may be given t-shirt sizes. You may give an estimated range for epic size in a number of days.
For example:
- Small = 1–4 days
- Medium = 5–10 days
- Large = 10–20 days
You can use this estimate and suppose that your first delivery of the product will take around 26-54 days.
The second round of planning
Once you have created a broad estimate it is time to do the second round of planning and develop the product backlog items corresponding to epics. The epics can be further broken down into user stories for sprints. Each PBI can be estimated with story points to get a more accurate estimate for the PBIs.
How to use T –shirt sizing to determine project scope
T-shirt estimation is a great way to understand the overall scope of your project. For example, a shopping list that is a small t-shirt size would mean buying a couple of items like a toothbrush and a cola, whereas a large t-shirt size idea would be buying fifty or more items from a shopping list. So, slotting these various tasks into t-shirt sizes will help the team understand the overall scope of the project and what must be accomplished. It helps to understand the effort required by each team member to accomplish the task.
Getting the Right Fit: The Do’s and Don'ts
T-shirt sizing, just like Agile, is not a one-size fits all method. Teams must figure out how to use it depending on their project and keeping in mind past projects and retrospectives.
There are some do’s and don’ts for t-shirt sizing that must be followed for success:
- Get the bigger picture: You can think big and dream during this process. Your result will be a rough estimate so you can let yourself go.
- Make sure to stick to the scope: It is easy to get derailed with so many ideas coming in from so many people. But make sure to keep your eye on the project goal and ensure that the sizing is getting you closer to the goal.
- Do not have too many sizes: This exercise is supposed to simplify your decision-making process, so there is no point in complicating it by adding too many t-shirt sizes.
- Do not get rigid with T-shirt labels: You can get creative with the names if you don’t want t-shirt names. Go for fruit names if you find it better! You can estimate in terms of a grape for the smallest stories and a pineapple for the larger ones. Alternatively, think of animals if your team likes them better. You can have everything from rabbits to giraffes to define your epics and sprints.
Assigning velocity for product backlog items
Development teams work around this by assigning each size a numerical value such as S=1, M=3, L=5, XL=8. Assigning numerical values makes it easier to calculate the velocity. So, if the team has completed 2 Small, 4 Medium, and 3 Large PBIs then the velocity can be calculated as:
- Velocity= S+M+L= (2*1)+(4*3)+(3*5)=29
T-Shirt sizing is fast.
T-shirt estimation allows an extremely fast, almost instant estimation with basic information. Compared to more absolute types of estimation that require more information from stakeholders and users and can result in considerable time consumption and effort, t-shirt sizing is quick and saves close to 80% times in some cases.
How does T-shirt sizing work?
T-shirt sizing starts off with the portfolio management team defining the size of the project, and they categorize the project as being extra small, small, medium, large, extra-large, etc. The product owner first gets together with the stakeholders and defines a few high-level epics. The epics are given t-shirt sizes based on their perceived complexity. The development team also uses historical data from previous projects to classify tasks into different-sized buckets.
T-shirt sizing is a great option for teams new to the whole estimating business. It is fast and simple, and teams can use it till they learn the ropes of the more accurate forms of estimation. Splitting projects into generalized buckets helps the team to break down complex tasks, helps in communication and allows the team to look at a long-term roadmap for the project. When done correctly, t-shirt sizing can boost productivity and save the team a whole lot of effort.
Delve into the most popular Agile Category Courses
Conclusion
T-shirt sizing in Agile, thus, offers a straightforward and collaborative approach to project estimation, especially useful in initial stages and in fostering team consensus, despite certain limitations in precision and dependence on team experience.
However, it's essential to remember that T-shirt sizing is a starting point, a way to initiate conversations about task complexity and team capacity. It is not a substitute for detailed planning or a definitive measure of effort and time. As the project progresses, teams should be prepared to adjust their estimates and plans based on more detailed analyses and emerging insights. KnowledgeHut Training will help you understand the basics of getting started with agile project management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How does T-shirt sizing differ from other estimation techniques in Agile?
2. Is T-shirt sizing suitable for all types of work items in Agile?
3. Can T-shirt sizing be applied to non-development work in Agile?
Get Free Consultation
By submitting, I accept the T&C and
Privacy Policy
Ready to lead with Scrum expertise?
